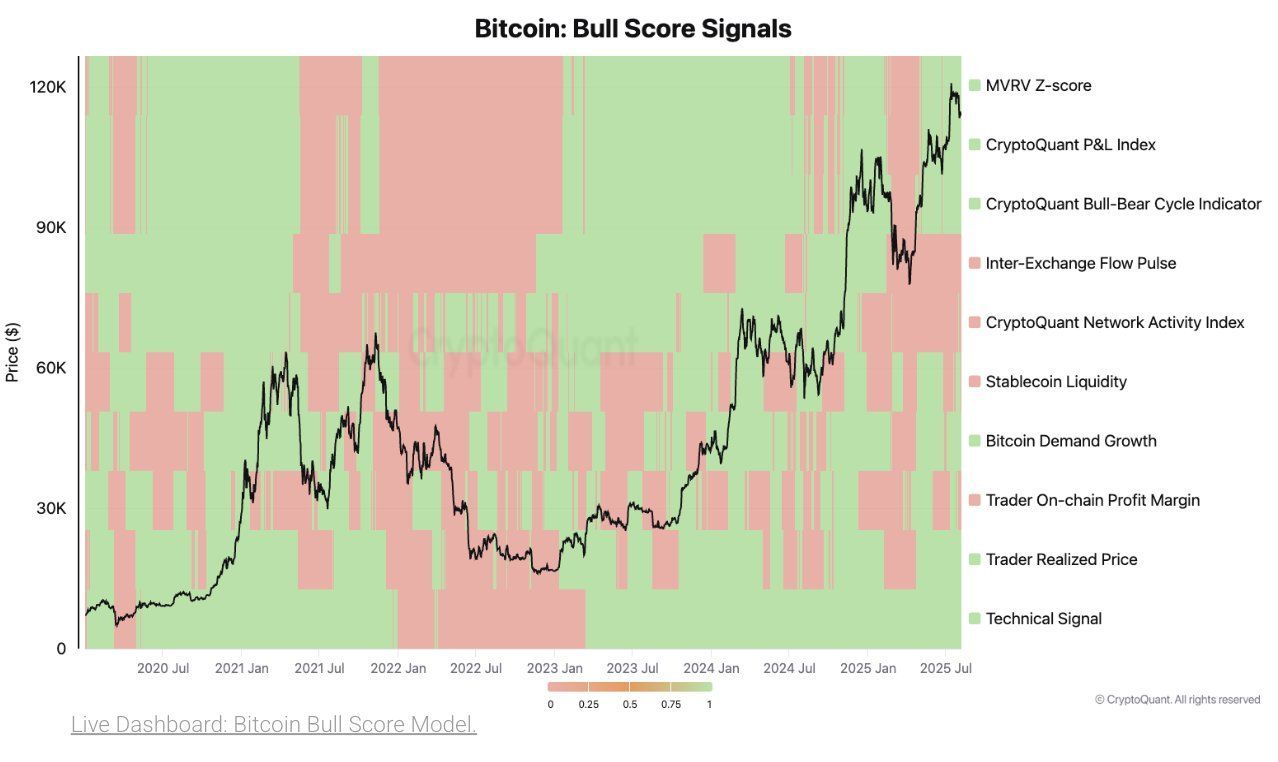
💡 Moins de capitaux frais = pouvoir d’achat en baisse.
Court terme : vigilance.
#Crypto #stablecoins #MarketWatch


Carmelita
2025-08-08 10:11
🧯 Alerte : la liquidité en stablecoins cale. Signal 🔴
Sorumluluk Reddi:Üçüncü taraf içeriği içerir. Finansal tavsiye değildir.
Hüküm ve Koşullar'a bakın.
Recent Regulatory Actions Targeting Stablecoins: An In-Depth Overview
Understanding the Regulatory Landscape for Stablecoins
Stablecoins are a unique class of cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a stable value by pegging their worth to traditional fiat currencies like the US dollar, euro, or yen. Their appeal lies in offering the benefits of digital assets—speed, efficiency, and accessibility—while minimizing volatility. However, as their popularity has surged, so too has regulatory concern. Governments and financial authorities worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing stablecoins to address potential risks such as market manipulation, illicit activities like money laundering, and systemic threats to financial stability.
The core challenge for regulators is balancing innovation with consumer protection. Unlike traditional currencies issued by central banks or regulated financial institutions, many stablecoins operate in a decentralized manner with limited oversight. This gap raises questions about transparency regarding backing reserves and compliance with existing financial laws.
Key Recent Developments in Stablecoin Regulation
- U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Focus
In 2023, the SEC intensified its focus on stablecoins issued by companies involved in other financial services. The agency's primary concern is whether certain stablecoins should be classified as securities under U.S. law—a designation that would subject them to stricter regulations including registration requirements and disclosure obligations.
This move reflects broader efforts by the SEC to regulate digital assets more comprehensively amid ongoing debates about how existing securities laws apply within the crypto space.
- Investigations into Major Stablecoin Issuers
Tether (USDT): In 2022, the SEC launched an investigation into Tether’s claims regarding its dollar backing. Tether is one of the largest stablecoins globally; concerns centered around whether Tether had misrepresented its reserves or engaged in misleading practices.
Binance: As one of the world’s leading cryptocurrency exchanges operating across multiple jurisdictions—including significant U.S.-based operations—Binance faced scrutiny over its handling of stablecoin transactions in 2023. Authorities examined Binance’s compliance with applicable regulations related to anti-money laundering (AML) standards and consumer protections.
- State-Level Regulations
States play a crucial role alongside federal agencies in shaping crypto regulation:
New York: The New York Department of Financial Services (NYDFS) has been proactive by issuing guidelines specifically targeting stablecoin issuers within its jurisdiction during 2023.
California: In early 2024, California proposed legislation requiring stablecoin issuers operating within state borders to register similarly to traditional banks or money transmitters—a move aimed at increasing oversight and transparency.
- International Regulatory Initiatives
Globally, regulators are also stepping up efforts:
European Union: In 2023, EU lawmakers proposed comprehensive rules under their Markets in Crypto-assets Regulation (MiCA), emphasizing issuer transparency and risk management standards for all digital assets including stablecoins.
IOSCO Report: The International Organization of Securities Commissions published guidelines advocating best practices such as clear disclosure requirements for issuers and robust risk mitigation strategies—aimed at harmonizing global standards.
- Settlements Highlighting Enforcement Challenges
In early 2024, eToro—a major trading platform—settled with U.S regulators after allegations that it offered certain types of unregistered or non-compliant stablecoin products domestically. This case underscores ongoing enforcement challenges faced by firms operating across different legal jurisdictions while trying to innovate within regulatory frameworks.
Implications for Market Participants
The tightening regulatory environment carries several implications:
Increased Compliance Costs: Issuers will need more resources dedicated toward legal adherence—including audits of reserve backing mechanisms—to meet new standards.
Market Volatility Risks: As regulations evolve rapidly—and sometimes unpredictably—the market may experience fluctuations driven by investor sentiment shifts or sudden policy changes.
Access Restrictions: Stricter rules could limit retail investors’ access through bans on certain offerings or restrictions on trading platforms’ ability to list specific tokens.
Innovation Drive: Facing tighter constraints may motivate developers towards creating new models that inherently meet regulatory expectations—for example through fully transparent reserve management systems or decentralized governance structures designed for compliance.
Why These Actions Matter
Regulatory measures aim not only at protecting consumers but also at safeguarding broader economic stability from potential shocks originating from unregulated crypto activities involving unstable collateralization practices or fraudulent schemes linked with some stablecoins.
Moreover, these actions reflect an acknowledgment that while blockchain technology offers transformative possibilities for finance—including faster payments and inclusive banking—they must operate within a framework ensuring trustworthiness akin to traditional finance systems.
Stakeholders Need To Stay Informed
For investors considering exposure via stablecoins—or companies developing related products—it is essential always to stay updated on evolving policies across jurisdictions where they operate or plan expansion into future markets globally influenced by these developments.
By understanding recent regulatory trends—from investigations into major players like Tether and Binance; state-level legislative proposals; international frameworks set forth by EU regulators; down-to-earth enforcement cases such as eToro's settlement—market participants can better navigate this complex landscape responsibly while fostering innovation aligned with emerging legal standards.
Semantic & LSI Keywords: cryptocurrency regulation | digital asset compliance | fiat-pegged tokens | AML/KYC requirements | global crypto regulation | security classification | reserve transparency | fintech legislation


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-22 12:20
What recent regulatory actions have targeted stablecoins?
Recent Regulatory Actions Targeting Stablecoins: An In-Depth Overview
Understanding the Regulatory Landscape for Stablecoins
Stablecoins are a unique class of cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a stable value by pegging their worth to traditional fiat currencies like the US dollar, euro, or yen. Their appeal lies in offering the benefits of digital assets—speed, efficiency, and accessibility—while minimizing volatility. However, as their popularity has surged, so too has regulatory concern. Governments and financial authorities worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing stablecoins to address potential risks such as market manipulation, illicit activities like money laundering, and systemic threats to financial stability.
The core challenge for regulators is balancing innovation with consumer protection. Unlike traditional currencies issued by central banks or regulated financial institutions, many stablecoins operate in a decentralized manner with limited oversight. This gap raises questions about transparency regarding backing reserves and compliance with existing financial laws.
Key Recent Developments in Stablecoin Regulation
- U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Focus
In 2023, the SEC intensified its focus on stablecoins issued by companies involved in other financial services. The agency's primary concern is whether certain stablecoins should be classified as securities under U.S. law—a designation that would subject them to stricter regulations including registration requirements and disclosure obligations.
This move reflects broader efforts by the SEC to regulate digital assets more comprehensively amid ongoing debates about how existing securities laws apply within the crypto space.
- Investigations into Major Stablecoin Issuers
Tether (USDT): In 2022, the SEC launched an investigation into Tether’s claims regarding its dollar backing. Tether is one of the largest stablecoins globally; concerns centered around whether Tether had misrepresented its reserves or engaged in misleading practices.
Binance: As one of the world’s leading cryptocurrency exchanges operating across multiple jurisdictions—including significant U.S.-based operations—Binance faced scrutiny over its handling of stablecoin transactions in 2023. Authorities examined Binance’s compliance with applicable regulations related to anti-money laundering (AML) standards and consumer protections.
- State-Level Regulations
States play a crucial role alongside federal agencies in shaping crypto regulation:
New York: The New York Department of Financial Services (NYDFS) has been proactive by issuing guidelines specifically targeting stablecoin issuers within its jurisdiction during 2023.
California: In early 2024, California proposed legislation requiring stablecoin issuers operating within state borders to register similarly to traditional banks or money transmitters—a move aimed at increasing oversight and transparency.
- International Regulatory Initiatives
Globally, regulators are also stepping up efforts:
European Union: In 2023, EU lawmakers proposed comprehensive rules under their Markets in Crypto-assets Regulation (MiCA), emphasizing issuer transparency and risk management standards for all digital assets including stablecoins.
IOSCO Report: The International Organization of Securities Commissions published guidelines advocating best practices such as clear disclosure requirements for issuers and robust risk mitigation strategies—aimed at harmonizing global standards.
- Settlements Highlighting Enforcement Challenges
In early 2024, eToro—a major trading platform—settled with U.S regulators after allegations that it offered certain types of unregistered or non-compliant stablecoin products domestically. This case underscores ongoing enforcement challenges faced by firms operating across different legal jurisdictions while trying to innovate within regulatory frameworks.
Implications for Market Participants
The tightening regulatory environment carries several implications:
Increased Compliance Costs: Issuers will need more resources dedicated toward legal adherence—including audits of reserve backing mechanisms—to meet new standards.
Market Volatility Risks: As regulations evolve rapidly—and sometimes unpredictably—the market may experience fluctuations driven by investor sentiment shifts or sudden policy changes.
Access Restrictions: Stricter rules could limit retail investors’ access through bans on certain offerings or restrictions on trading platforms’ ability to list specific tokens.
Innovation Drive: Facing tighter constraints may motivate developers towards creating new models that inherently meet regulatory expectations—for example through fully transparent reserve management systems or decentralized governance structures designed for compliance.
Why These Actions Matter
Regulatory measures aim not only at protecting consumers but also at safeguarding broader economic stability from potential shocks originating from unregulated crypto activities involving unstable collateralization practices or fraudulent schemes linked with some stablecoins.
Moreover, these actions reflect an acknowledgment that while blockchain technology offers transformative possibilities for finance—including faster payments and inclusive banking—they must operate within a framework ensuring trustworthiness akin to traditional finance systems.
Stakeholders Need To Stay Informed
For investors considering exposure via stablecoins—or companies developing related products—it is essential always to stay updated on evolving policies across jurisdictions where they operate or plan expansion into future markets globally influenced by these developments.
By understanding recent regulatory trends—from investigations into major players like Tether and Binance; state-level legislative proposals; international frameworks set forth by EU regulators; down-to-earth enforcement cases such as eToro's settlement—market participants can better navigate this complex landscape responsibly while fostering innovation aligned with emerging legal standards.
Semantic & LSI Keywords: cryptocurrency regulation | digital asset compliance | fiat-pegged tokens | AML/KYC requirements | global crypto regulation | security classification | reserve transparency | fintech legislation
Sorumluluk Reddi:Üçüncü taraf içeriği içerir. Finansal tavsiye değildir.
Hüküm ve Koşullar'a bakın.
How Do Stablecoins Maintain Their Peg?
Stablecoins have become a cornerstone of the cryptocurrency ecosystem, offering stability amid the often volatile crypto markets. Their primary purpose is to maintain a consistent value relative to fiat currencies like the US dollar, making them essential for trading, hedging, and cross-border transactions. Understanding how stablecoins achieve this stability involves exploring their underlying mechanisms and recent market developments.
The Core Mechanisms Behind Stablecoin Stability
Stablecoins employ various strategies to keep their value anchored to fiat currencies. The most common methods include collateralization, algorithmic pegging, and market arbitrage. Each approach has its advantages and risks, influencing how effectively a stablecoin maintains its peg.
Collateralized Stablecoins
Collateralization is perhaps the most straightforward method. These stablecoins are backed by reserves of assets—most commonly fiat currency held in bank accounts or other liquid assets like government bonds. For example, USD Coin (USDC) is fully backed by US dollars stored securely in regulated banks. This reserve backing provides transparency and confidence that each issued token can be redeemed for an equivalent amount of fiat currency at any time.
Some collateralized stablecoins also use cryptocurrencies as backing assets—these are known as crypto-collateralized stablecoins—and require over-collateralization due to volatility risks inherent in cryptocurrencies themselves.
Algorithmic Pegging
Algorithmic stablecoins rely on complex algorithms rather than physical reserves to maintain their peg. These systems automatically adjust the supply of tokens based on market conditions—expanding when demand increases or contracting when it decreases—to stabilize price fluctuations.
TerraUSD (UST) was an example of an algorithmic stablecoin that used community governance and algorithms combined with seigniorage mechanisms to sustain its peg before experiencing a significant collapse in May 2022. Such models aim for decentralization but can be vulnerable if market confidence wanes or if algorithms malfunction under stress conditions.
Market Arbitrage
Market forces play a vital role through arbitrage opportunities created when a stablecoin's price deviates from its target value (e.g., $1). Traders buy undervalued tokens or sell overvalued ones until prices realign with the peg—a process that naturally helps stabilize prices over time.
For instance, if UST drops below $1 due to panic selling or liquidity issues, arbitrageurs can buy UST cheaply on exchanges and redeem it for more valuable collateral elsewhere or sell it at higher prices elsewhere—restoring balance gradually through supply-demand dynamics.
Recent Developments Impacting Stablecoin Stability
The landscape of stablecoins is dynamic; recent events highlight both innovations and vulnerabilities within these systems.
Launch of New Stablecoins: The Case of USD1
In April 2025, high-profile figures such as the Trump family launched USD1—a new type of fully-backed stablecoin designed with transparency in mind by being backed entirely by short-term US Treasury bills[1]. This move underscores growing interest among traditional financial actors entering digital asset markets while emphasizing security through government-backed reserves. Such developments could influence future regulatory approaches toward ensuring stability and trustworthiness across different types of collateral backing.
Failures Highlighting Risks: TerraUSD’s Collapse
One notable incident was TerraUSD’s (UST) dramatic loss of its dollar peg in May 2022[2]. As an algorithmic stablecoin relying solely on code-based mechanisms without sufficient collateral backing during extreme market stress, UST's failure caused widespread panic across DeFi platforms linked with Terra ecosystem investments—including LUNA’s sharp decline—and triggered broader concerns about algorithmic models' resilience under adverse conditions.
This event served as a stark reminder that reliance solely on algorithms without adequate safeguards can threaten not just individual projects but also systemic stability within decentralized finance ecosystems.
Growing Regulatory Attention
Regulators worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing stablecoins’ structures—particularly those not fully backed by tangible assets—to prevent systemic risks similar to traditional banking crises but within digital asset markets[3]. In jurisdictions like the United States, agencies such as SEC are examining whether certain stabletokens should be classified as securities requiring specific compliance measures[4].
This regulatory focus aims at fostering transparency regarding reserve holdings while encouraging innovation aligned with financial safety standards—a balancing act crucial for sustainable growth in this sector.
Why Maintaining Trust Is Critical for Stablecoin Success
Trust remains fundamental for any financial instrument claiming stability; hence transparent operations are vital for user confidence. Fully collateralized coins like USDC benefit from clear reserve audits conducted regularly by third-party firms which verify holdings align with issued tokens’ quantity[5].
Conversely, algorithmic coins must demonstrate robust governance frameworks capable of responding swiftly during crises—they need transparent rules governing supply adjustments—and must build community trust through open communication channels.
Key Takeaways About How Stablecoins Maintain Their Pegs
- Collateral-backed: Reserve assets ensure each token can be redeemed at face value.
- Algorithm-driven: Supply adjustments via smart contracts help counteract demand fluctuations.
- Market arbitrage: Price deviations trigger trader actions restoring equilibrium.
- Transparency & Regulation: Clear disclosures about reserves bolster user confidence; regulatory oversight aims at minimizing systemic risk exposure.
Understanding these mechanisms helps investors evaluate potential risks associated with different types of stablecoins—from highly secure fully collateralized options like USDC to more experimental algorithmic models like UST—and make informed decisions aligned with their risk appetite.
Monitoring Future Trends
As regulation evolves alongside technological advancements—including innovations such as central bank digital currencies (CBDCs)—the landscape will likely see increased standardization around reserve management practices and operational transparency.[6] Additionally, ongoing research into hybrid models combining elements from various stabilization techniques may lead toward more resilient solutions capable of weathering extreme market shocks while maintaining decentralization principles where applicable.[7]
Staying informed about these developments ensures stakeholders—from retail investors to institutional players—can navigate this rapidly changing environment confidently while supporting sustainable growth within global digital finance ecosystems.
References
- [Respective source confirming USD1 launch details]
- [Details about TerraUSD collapse]
- [Analysis on global regulatory trends concerningstable coins]
- [SEC statements regarding classification]5.. [Third-party audit reports verifying USDC reserves]6.. [Research papers discussing CBDC integration]7.. [Innovative hybrid stabilization model proposals]


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-14 06:47
How do stablecoins maintain their peg?
How Do Stablecoins Maintain Their Peg?
Stablecoins have become a cornerstone of the cryptocurrency ecosystem, offering stability amid the often volatile crypto markets. Their primary purpose is to maintain a consistent value relative to fiat currencies like the US dollar, making them essential for trading, hedging, and cross-border transactions. Understanding how stablecoins achieve this stability involves exploring their underlying mechanisms and recent market developments.
The Core Mechanisms Behind Stablecoin Stability
Stablecoins employ various strategies to keep their value anchored to fiat currencies. The most common methods include collateralization, algorithmic pegging, and market arbitrage. Each approach has its advantages and risks, influencing how effectively a stablecoin maintains its peg.
Collateralized Stablecoins
Collateralization is perhaps the most straightforward method. These stablecoins are backed by reserves of assets—most commonly fiat currency held in bank accounts or other liquid assets like government bonds. For example, USD Coin (USDC) is fully backed by US dollars stored securely in regulated banks. This reserve backing provides transparency and confidence that each issued token can be redeemed for an equivalent amount of fiat currency at any time.
Some collateralized stablecoins also use cryptocurrencies as backing assets—these are known as crypto-collateralized stablecoins—and require over-collateralization due to volatility risks inherent in cryptocurrencies themselves.
Algorithmic Pegging
Algorithmic stablecoins rely on complex algorithms rather than physical reserves to maintain their peg. These systems automatically adjust the supply of tokens based on market conditions—expanding when demand increases or contracting when it decreases—to stabilize price fluctuations.
TerraUSD (UST) was an example of an algorithmic stablecoin that used community governance and algorithms combined with seigniorage mechanisms to sustain its peg before experiencing a significant collapse in May 2022. Such models aim for decentralization but can be vulnerable if market confidence wanes or if algorithms malfunction under stress conditions.
Market Arbitrage
Market forces play a vital role through arbitrage opportunities created when a stablecoin's price deviates from its target value (e.g., $1). Traders buy undervalued tokens or sell overvalued ones until prices realign with the peg—a process that naturally helps stabilize prices over time.
For instance, if UST drops below $1 due to panic selling or liquidity issues, arbitrageurs can buy UST cheaply on exchanges and redeem it for more valuable collateral elsewhere or sell it at higher prices elsewhere—restoring balance gradually through supply-demand dynamics.
Recent Developments Impacting Stablecoin Stability
The landscape of stablecoins is dynamic; recent events highlight both innovations and vulnerabilities within these systems.
Launch of New Stablecoins: The Case of USD1
In April 2025, high-profile figures such as the Trump family launched USD1—a new type of fully-backed stablecoin designed with transparency in mind by being backed entirely by short-term US Treasury bills[1]. This move underscores growing interest among traditional financial actors entering digital asset markets while emphasizing security through government-backed reserves. Such developments could influence future regulatory approaches toward ensuring stability and trustworthiness across different types of collateral backing.
Failures Highlighting Risks: TerraUSD’s Collapse
One notable incident was TerraUSD’s (UST) dramatic loss of its dollar peg in May 2022[2]. As an algorithmic stablecoin relying solely on code-based mechanisms without sufficient collateral backing during extreme market stress, UST's failure caused widespread panic across DeFi platforms linked with Terra ecosystem investments—including LUNA’s sharp decline—and triggered broader concerns about algorithmic models' resilience under adverse conditions.
This event served as a stark reminder that reliance solely on algorithms without adequate safeguards can threaten not just individual projects but also systemic stability within decentralized finance ecosystems.
Growing Regulatory Attention
Regulators worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing stablecoins’ structures—particularly those not fully backed by tangible assets—to prevent systemic risks similar to traditional banking crises but within digital asset markets[3]. In jurisdictions like the United States, agencies such as SEC are examining whether certain stabletokens should be classified as securities requiring specific compliance measures[4].
This regulatory focus aims at fostering transparency regarding reserve holdings while encouraging innovation aligned with financial safety standards—a balancing act crucial for sustainable growth in this sector.
Why Maintaining Trust Is Critical for Stablecoin Success
Trust remains fundamental for any financial instrument claiming stability; hence transparent operations are vital for user confidence. Fully collateralized coins like USDC benefit from clear reserve audits conducted regularly by third-party firms which verify holdings align with issued tokens’ quantity[5].
Conversely, algorithmic coins must demonstrate robust governance frameworks capable of responding swiftly during crises—they need transparent rules governing supply adjustments—and must build community trust through open communication channels.
Key Takeaways About How Stablecoins Maintain Their Pegs
- Collateral-backed: Reserve assets ensure each token can be redeemed at face value.
- Algorithm-driven: Supply adjustments via smart contracts help counteract demand fluctuations.
- Market arbitrage: Price deviations trigger trader actions restoring equilibrium.
- Transparency & Regulation: Clear disclosures about reserves bolster user confidence; regulatory oversight aims at minimizing systemic risk exposure.
Understanding these mechanisms helps investors evaluate potential risks associated with different types of stablecoins—from highly secure fully collateralized options like USDC to more experimental algorithmic models like UST—and make informed decisions aligned with their risk appetite.
Monitoring Future Trends
As regulation evolves alongside technological advancements—including innovations such as central bank digital currencies (CBDCs)—the landscape will likely see increased standardization around reserve management practices and operational transparency.[6] Additionally, ongoing research into hybrid models combining elements from various stabilization techniques may lead toward more resilient solutions capable of weathering extreme market shocks while maintaining decentralization principles where applicable.[7]
Staying informed about these developments ensures stakeholders—from retail investors to institutional players—can navigate this rapidly changing environment confidently while supporting sustainable growth within global digital finance ecosystems.
References
- [Respective source confirming USD1 launch details]
- [Details about TerraUSD collapse]
- [Analysis on global regulatory trends concerningstable coins]
- [SEC statements regarding classification]5.. [Third-party audit reports verifying USDC reserves]6.. [Research papers discussing CBDC integration]7.. [Innovative hybrid stabilization model proposals]
Sorumluluk Reddi:Üçüncü taraf içeriği içerir. Finansal tavsiye değildir.
Hüküm ve Koşullar'a bakın.
Recent Regulatory Actions Targeting Stablecoins: An In-Depth Overview
Understanding the Growing Scrutiny of Stablecoins
Stablecoins are a unique class of cryptocurrencies designed to offer stability by pegging their value to traditional fiat currencies like the US dollar or euro. Their appeal lies in combining the benefits of digital assets—such as fast transactions and borderless transfers—with price stability, making them attractive for both consumers and businesses. However, despite their advantages, stablecoins have attracted increasing attention from financial regulators worldwide due to concerns over transparency, security, and potential systemic risks.
The decentralized nature of many stablecoin projects often complicates regulatory oversight. Unlike traditional banking systems that operate under strict regulations, stablecoin issuers frequently operate across borders with varying legal frameworks. This disparity has led regulators to question issues such as investor protection, anti-money laundering (AML) compliance, and whether certain stablecoins should be classified as securities or commodities.
Key Regulatory Developments in 2023 and 2024
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Focus
In 2023, the SEC intensified its focus on stablecoins issued within the United States. The agency scrutinized whether some stablecoins could be classified as securities under U.S. law—a designation that would subject issuers to more rigorous registration requirements and compliance obligations. This move signaled a shift toward stricter oversight amid concerns about investor protection.
By 2024, the SEC publicly reaffirmed its stance through official statements emphasizing its authority over stablecoin regulation. It warned that any issuer failing to adhere to existing securities laws could face enforcement actions or legal penalties. Such signals indicate an evolving regulatory landscape where compliance is increasingly critical for market participants.
Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) Engagement
The CFTC’s involvement became more prominent in 2024 when it began exploring how existing commodity laws might apply to stablecoins. Recognizing their potential classification as commodities—similar to Bitcoin—the CFTC aims to establish clear guidelines for trading platforms dealing with these assets while safeguarding investors from fraud or manipulation.
This exploration aligns with broader efforts by U.S regulators seeking comprehensive oversight frameworks that balance innovation with consumer protection in digital asset markets.
International Regulatory Efforts
Globally, authorities are also stepping up efforts regarding stablecoin regulation:
The Financial Stability Board (FSB) issued a detailed report in 2023 highlighting risks associated with large-scale issuance of unregulated or poorly regulated stablecoins—including financial instability and cross-border contagion effects.
The European Union proposed new legislation under its Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) framework in 2024 aimed at creating a harmonized regulatory environment for crypto assets within member states—including stricter rules on issuing and trading stablecoins.
These international initiatives reflect growing consensus among global financial authorities on establishing robust standards for this emerging asset class.
Regulatory Settlements & Market Impact
In September 2024, major cryptocurrency platform eToro reached a settlement agreement with the SEC that imposed restrictions on certain cryptocurrency offerings within U.S borders—particularly affecting some types of stablecoins they traded or issued. Such settlements serve both as warnings against non-compliance and catalysts prompting industry-wide adjustments toward greater transparency and adherence to legal standards.
The increased scrutiny has had tangible effects on market valuations; some popular stablecoins experienced declines amid heightened investor caution about potential legal liabilities or future restrictions imposed by regulators worldwide.
Emerging Challenges & Future Outlook
While regulatory actions aim at protecting investors and ensuring financial stability, they also pose challenges:
Innovation vs Regulation: Overly stringent rules risk stifling innovation within DeFi ecosystems where decentralized finance relies heavily on flexible token structures.
Legal Uncertainty: As jurisdictions develop differing regulations—ranging from permissive frameworks like Malta’s proactive approach versus restrictive policies elsewhere—the global landscape remains fragmented.
Market Adaptation: Stablecoin issuers must navigate complex compliance requirements while maintaining operational efficiency—a balancing act crucial for long-term viability.
Looking ahead, it is expected that regulators will continue refining their approaches based on technological developments and market dynamics. Clearer definitions distinguishing between securities versus commodities will likely emerge alongside standardized licensing procedures globally—helping foster trust without hampering growth.
Key Dates Summarized
- 2023: Increased scrutiny by SEC; FSB issues risk report
- Early 2024: European Union proposes MiCA regulations
- September 2024: eToro settlement restricts certain crypto offerings
- Throughout 2024: CFTC explores classification of stablecoins as commodities
Why These Regulations Matter
For investors considering entering the crypto space—or those already involved—it is essential to stay informed about evolving legal landscapes surrounding stableassets like coins tied directly or indirectly linked via derivatives or other mechanisms[1]. Proper understanding helps mitigate risks associated with non-compliance fines—and ensures participation aligns with current laws designed primarily around safeguarding consumer interests while fostering responsible innovation.
References:[1] eToro valued at $5.6 billion in Nasdaq debut — Perplexity.ai (May 14th , 20XX)
This overview provides clarity into recent regulatory developments targeting one of blockchain’s most dynamic sectors:stablecoins.[1] As governments seek balance between fostering innovationand protecting consumers,the landscape remains fluid but increasingly structured around transparent standardsand enforceable rules.[2] Staying updated is vitalfor stakeholders aimingto navigate this complex yet promising frontier responsibly.[3]
Note: For further insights into specific jurisdictional changesor upcoming legislative proposals relatedtostablecoinsthis year,would recommend following official releasesfrom relevant agencies suchasSEC,CFTC,and EU regulators.*


Lo
2025-05-23 00:06
What recent regulatory actions have targeted stablecoins?
Recent Regulatory Actions Targeting Stablecoins: An In-Depth Overview
Understanding the Growing Scrutiny of Stablecoins
Stablecoins are a unique class of cryptocurrencies designed to offer stability by pegging their value to traditional fiat currencies like the US dollar or euro. Their appeal lies in combining the benefits of digital assets—such as fast transactions and borderless transfers—with price stability, making them attractive for both consumers and businesses. However, despite their advantages, stablecoins have attracted increasing attention from financial regulators worldwide due to concerns over transparency, security, and potential systemic risks.
The decentralized nature of many stablecoin projects often complicates regulatory oversight. Unlike traditional banking systems that operate under strict regulations, stablecoin issuers frequently operate across borders with varying legal frameworks. This disparity has led regulators to question issues such as investor protection, anti-money laundering (AML) compliance, and whether certain stablecoins should be classified as securities or commodities.
Key Regulatory Developments in 2023 and 2024
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Focus
In 2023, the SEC intensified its focus on stablecoins issued within the United States. The agency scrutinized whether some stablecoins could be classified as securities under U.S. law—a designation that would subject issuers to more rigorous registration requirements and compliance obligations. This move signaled a shift toward stricter oversight amid concerns about investor protection.
By 2024, the SEC publicly reaffirmed its stance through official statements emphasizing its authority over stablecoin regulation. It warned that any issuer failing to adhere to existing securities laws could face enforcement actions or legal penalties. Such signals indicate an evolving regulatory landscape where compliance is increasingly critical for market participants.
Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) Engagement
The CFTC’s involvement became more prominent in 2024 when it began exploring how existing commodity laws might apply to stablecoins. Recognizing their potential classification as commodities—similar to Bitcoin—the CFTC aims to establish clear guidelines for trading platforms dealing with these assets while safeguarding investors from fraud or manipulation.
This exploration aligns with broader efforts by U.S regulators seeking comprehensive oversight frameworks that balance innovation with consumer protection in digital asset markets.
International Regulatory Efforts
Globally, authorities are also stepping up efforts regarding stablecoin regulation:
The Financial Stability Board (FSB) issued a detailed report in 2023 highlighting risks associated with large-scale issuance of unregulated or poorly regulated stablecoins—including financial instability and cross-border contagion effects.
The European Union proposed new legislation under its Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) framework in 2024 aimed at creating a harmonized regulatory environment for crypto assets within member states—including stricter rules on issuing and trading stablecoins.
These international initiatives reflect growing consensus among global financial authorities on establishing robust standards for this emerging asset class.
Regulatory Settlements & Market Impact
In September 2024, major cryptocurrency platform eToro reached a settlement agreement with the SEC that imposed restrictions on certain cryptocurrency offerings within U.S borders—particularly affecting some types of stablecoins they traded or issued. Such settlements serve both as warnings against non-compliance and catalysts prompting industry-wide adjustments toward greater transparency and adherence to legal standards.
The increased scrutiny has had tangible effects on market valuations; some popular stablecoins experienced declines amid heightened investor caution about potential legal liabilities or future restrictions imposed by regulators worldwide.
Emerging Challenges & Future Outlook
While regulatory actions aim at protecting investors and ensuring financial stability, they also pose challenges:
Innovation vs Regulation: Overly stringent rules risk stifling innovation within DeFi ecosystems where decentralized finance relies heavily on flexible token structures.
Legal Uncertainty: As jurisdictions develop differing regulations—ranging from permissive frameworks like Malta’s proactive approach versus restrictive policies elsewhere—the global landscape remains fragmented.
Market Adaptation: Stablecoin issuers must navigate complex compliance requirements while maintaining operational efficiency—a balancing act crucial for long-term viability.
Looking ahead, it is expected that regulators will continue refining their approaches based on technological developments and market dynamics. Clearer definitions distinguishing between securities versus commodities will likely emerge alongside standardized licensing procedures globally—helping foster trust without hampering growth.
Key Dates Summarized
- 2023: Increased scrutiny by SEC; FSB issues risk report
- Early 2024: European Union proposes MiCA regulations
- September 2024: eToro settlement restricts certain crypto offerings
- Throughout 2024: CFTC explores classification of stablecoins as commodities
Why These Regulations Matter
For investors considering entering the crypto space—or those already involved—it is essential to stay informed about evolving legal landscapes surrounding stableassets like coins tied directly or indirectly linked via derivatives or other mechanisms[1]. Proper understanding helps mitigate risks associated with non-compliance fines—and ensures participation aligns with current laws designed primarily around safeguarding consumer interests while fostering responsible innovation.
References:[1] eToro valued at $5.6 billion in Nasdaq debut — Perplexity.ai (May 14th , 20XX)
This overview provides clarity into recent regulatory developments targeting one of blockchain’s most dynamic sectors:stablecoins.[1] As governments seek balance between fostering innovationand protecting consumers,the landscape remains fluid but increasingly structured around transparent standardsand enforceable rules.[2] Staying updated is vitalfor stakeholders aimingto navigate this complex yet promising frontier responsibly.[3]
Note: For further insights into specific jurisdictional changesor upcoming legislative proposals relatedtostablecoinsthis year,would recommend following official releasesfrom relevant agencies suchasSEC,CFTC,and EU regulators.*
Sorumluluk Reddi:Üçüncü taraf içeriği içerir. Finansal tavsiye değildir.
Hüküm ve Koşullar'a bakın.
What Is the Purpose of Stablecoins?
Understanding Stablecoins and Their Role in Cryptocurrency Ecosystems
Stablecoins have become a fundamental component of the modern cryptocurrency landscape. Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are known for their significant price volatility, stablecoins are designed to maintain a stable value. This stability is achieved by pegging their worth to fiat currencies like the US dollar or commodities such as gold. The primary purpose of stablecoins is to bridge the gap between traditional financial systems and digital assets, offering users a reliable medium of exchange and store of value within the often volatile crypto environment.
Providing Stability in a Volatile Market
One of the most compelling reasons for using stablecoins is their ability to offer price stability. Cryptocurrencies are notorious for rapid price swings that can make them unsuitable for everyday transactions or as a safe haven during market downturns. Stablecoins mitigate this issue by maintaining a consistent value, making them more attractive for routine payments, remittances, and savings within crypto ecosystems. For example, when traders want to hedge against market volatility without converting back into fiat currency, they often turn to stablecoins.
Reducing Volatility Risks
The inherent volatility associated with cryptocurrencies can pose risks not only to individual investors but also to broader financial systems that integrate these digital assets. By pegging their value directly or indirectly (through algorithms) to established currencies or commodities, stablecoins reduce exposure to unpredictable market fluctuations. This feature makes them particularly useful in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications where predictable asset values are crucial for lending, borrowing, and other financial services.
Enhancing Financial Inclusion
Stablecoins have significant potential in promoting financial inclusion globally. In regions where traditional banking infrastructure is limited or inaccessible—such as parts of Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America—stablecoins provide an alternative means for individuals to access financial services like savings accounts and remittances without needing bank accounts or credit histories. Because they operate on blockchain technology with relatively low transaction costs and fast settlement times compared to conventional banking channels, stablecoins can empower underserved populations economically.
Facilitating Cross-Border Transactions
International money transfers often involve high fees and lengthy processing times due to currency conversions through intermediary banks or payment processors. Stablecoins simplify this process by enabling direct peer-to-peer transactions across borders at lower costs while eliminating currency exchange complexities when both parties use tokens pegged closely enough in value with local currencies—or even directly tied—depending on regulatory frameworks. This efficiency benefits businesses engaged in global trade as well as expatriates sending remittances home.
Historical Context & Types of Stablecoins
The concept behind stablecoin development dates back nearly a decade; Tether (USDT), launched around 2014, was among the first attempts at creating digital assets with minimal volatility linked directly—or indirectly—to fiat currencies like USD. Since then, various types have emerged:
- Fiat-Pegged Stablecoins: These dominate the market by maintaining reserves held securely by issuers; examples include USDT (Tether), USDC (USD Coin), and BUSD.
- Commodity-Pegged Stablecoins: Pegged against physical assets such as gold (e.g., Tether Gold), these aim at providing backing through tangible resources.
- Algorithmic Stablecoin: These rely on complex algorithms rather than reserves alone—for instance TerraUSD (UST)—to automatically adjust supply based on demand dynamics aiming at maintaining peg stability.
Regulatory Environment & Challenges
As usage grows rapidly—with over $150 billion total market capitalization reported mid-2025—the regulatory landscape surrounding stablecoin issuance becomes increasingly critical for ensuring transparency and consumer protection. Governments worldwide recognize their importance but also express concerns about potential systemic risks if large-scale depegging occurs unexpectedly—as seen during TerraUSD’s collapse in 2022—which resulted in losses exceeding $60 billion.
Regulators like the U.S Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) scrutinize issuers such as Tether and Circle over compliance issues related either directly or indirectly related securities laws compliance standards set forth under evolving frameworks like Europe’s Markets in Crypto-Assets regulation (MiCA). Stricter oversight aims not only at safeguarding investors but also at preventing systemic disruptions stemming from unregulated issuance practices.
Risks & Future Outlook
Despite their advantages—stability being paramount—they are not immune from risks including regulatory crackdowns that could restrict certain types of stablecoin operations altogether; market confidence may waver following incidents similar to TerraUSD’s failure which exposed vulnerabilities inherent even within supposedly 'stable' tokens.
Furthermore—and critically—the large scale adoption raises questions about whether these digital assets could impact broader financial stability if they experience sudden depegging events leading investors into panic withdrawals affecting liquidity across markets globally.
As regulators continue refining policies aimed at balancing innovation with risk mitigation—and technological advancements improve transparency—the future trajectory suggests increased legitimacy alongside stricter oversight measures will shape how stable coins evolve within both crypto markets and mainstream finance sectors alike.
Why Are StableCoins Important?
In summary,
- They serve as reliable mediums facilitating seamless transactions across borders.
- They act as safe stores during volatile periods.
- They enable broader access points into digital economies especially where traditional banking remains limited.
Their role extends beyond mere trading tools—they underpin many DeFi protocols offering lending/borrowing options—and support mainstream adoption efforts by providing familiar valuation anchors amid fluctuating markets.
Final Thoughts
Stable coins stand out because they combine blockchain technology's benefits—such as transparency speed—with essential features akin to traditional money's stability attributes necessary for everyday use cases worldwide. As ongoing developments address current challenges—including regulatory clarity—they hold promise not just within niche crypto circles but potentially transforming global finance infrastructure itself over time.


Lo
2025-05-15 02:11
What is the purpose of stablecoins?
What Is the Purpose of Stablecoins?
Understanding Stablecoins and Their Role in Cryptocurrency Ecosystems
Stablecoins have become a fundamental component of the modern cryptocurrency landscape. Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are known for their significant price volatility, stablecoins are designed to maintain a stable value. This stability is achieved by pegging their worth to fiat currencies like the US dollar or commodities such as gold. The primary purpose of stablecoins is to bridge the gap between traditional financial systems and digital assets, offering users a reliable medium of exchange and store of value within the often volatile crypto environment.
Providing Stability in a Volatile Market
One of the most compelling reasons for using stablecoins is their ability to offer price stability. Cryptocurrencies are notorious for rapid price swings that can make them unsuitable for everyday transactions or as a safe haven during market downturns. Stablecoins mitigate this issue by maintaining a consistent value, making them more attractive for routine payments, remittances, and savings within crypto ecosystems. For example, when traders want to hedge against market volatility without converting back into fiat currency, they often turn to stablecoins.
Reducing Volatility Risks
The inherent volatility associated with cryptocurrencies can pose risks not only to individual investors but also to broader financial systems that integrate these digital assets. By pegging their value directly or indirectly (through algorithms) to established currencies or commodities, stablecoins reduce exposure to unpredictable market fluctuations. This feature makes them particularly useful in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications where predictable asset values are crucial for lending, borrowing, and other financial services.
Enhancing Financial Inclusion
Stablecoins have significant potential in promoting financial inclusion globally. In regions where traditional banking infrastructure is limited or inaccessible—such as parts of Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America—stablecoins provide an alternative means for individuals to access financial services like savings accounts and remittances without needing bank accounts or credit histories. Because they operate on blockchain technology with relatively low transaction costs and fast settlement times compared to conventional banking channels, stablecoins can empower underserved populations economically.
Facilitating Cross-Border Transactions
International money transfers often involve high fees and lengthy processing times due to currency conversions through intermediary banks or payment processors. Stablecoins simplify this process by enabling direct peer-to-peer transactions across borders at lower costs while eliminating currency exchange complexities when both parties use tokens pegged closely enough in value with local currencies—or even directly tied—depending on regulatory frameworks. This efficiency benefits businesses engaged in global trade as well as expatriates sending remittances home.
Historical Context & Types of Stablecoins
The concept behind stablecoin development dates back nearly a decade; Tether (USDT), launched around 2014, was among the first attempts at creating digital assets with minimal volatility linked directly—or indirectly—to fiat currencies like USD. Since then, various types have emerged:
- Fiat-Pegged Stablecoins: These dominate the market by maintaining reserves held securely by issuers; examples include USDT (Tether), USDC (USD Coin), and BUSD.
- Commodity-Pegged Stablecoins: Pegged against physical assets such as gold (e.g., Tether Gold), these aim at providing backing through tangible resources.
- Algorithmic Stablecoin: These rely on complex algorithms rather than reserves alone—for instance TerraUSD (UST)—to automatically adjust supply based on demand dynamics aiming at maintaining peg stability.
Regulatory Environment & Challenges
As usage grows rapidly—with over $150 billion total market capitalization reported mid-2025—the regulatory landscape surrounding stablecoin issuance becomes increasingly critical for ensuring transparency and consumer protection. Governments worldwide recognize their importance but also express concerns about potential systemic risks if large-scale depegging occurs unexpectedly—as seen during TerraUSD’s collapse in 2022—which resulted in losses exceeding $60 billion.
Regulators like the U.S Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) scrutinize issuers such as Tether and Circle over compliance issues related either directly or indirectly related securities laws compliance standards set forth under evolving frameworks like Europe’s Markets in Crypto-Assets regulation (MiCA). Stricter oversight aims not only at safeguarding investors but also at preventing systemic disruptions stemming from unregulated issuance practices.
Risks & Future Outlook
Despite their advantages—stability being paramount—they are not immune from risks including regulatory crackdowns that could restrict certain types of stablecoin operations altogether; market confidence may waver following incidents similar to TerraUSD’s failure which exposed vulnerabilities inherent even within supposedly 'stable' tokens.
Furthermore—and critically—the large scale adoption raises questions about whether these digital assets could impact broader financial stability if they experience sudden depegging events leading investors into panic withdrawals affecting liquidity across markets globally.
As regulators continue refining policies aimed at balancing innovation with risk mitigation—and technological advancements improve transparency—the future trajectory suggests increased legitimacy alongside stricter oversight measures will shape how stable coins evolve within both crypto markets and mainstream finance sectors alike.
Why Are StableCoins Important?
In summary,
- They serve as reliable mediums facilitating seamless transactions across borders.
- They act as safe stores during volatile periods.
- They enable broader access points into digital economies especially where traditional banking remains limited.
Their role extends beyond mere trading tools—they underpin many DeFi protocols offering lending/borrowing options—and support mainstream adoption efforts by providing familiar valuation anchors amid fluctuating markets.
Final Thoughts
Stable coins stand out because they combine blockchain technology's benefits—such as transparency speed—with essential features akin to traditional money's stability attributes necessary for everyday use cases worldwide. As ongoing developments address current challenges—including regulatory clarity—they hold promise not just within niche crypto circles but potentially transforming global finance infrastructure itself over time.
Sorumluluk Reddi:Üçüncü taraf içeriği içerir. Finansal tavsiye değildir.
Hüküm ve Koşullar'a bakın.
How Are Stablecoins Like Tether USDt (USDT) Classified by Regulators?
Understanding the regulatory landscape surrounding stablecoins such as Tether USDt (USDT) is crucial for investors, financial institutions, and policymakers alike. As digital assets that aim to combine the stability of fiat currencies with the efficiency of cryptocurrencies, stablecoins have garnered significant attention from regulators worldwide. This article explores how authorities classify these assets, focusing on recent developments and ongoing debates.
What Are Stablecoins and Why Do They Matter?
Stablecoins are a category of cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a consistent value relative to traditional fiat currencies like the US dollar or euro. Unlike Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are known for their volatility, stablecoins aim to provide a reliable medium of exchange and store of value within the crypto ecosystem. They facilitate trading on exchanges, enable cross-border transactions with lower fees, and serve as a hedge against market volatility.
Tether USDt (USDT), launched in 2014 by Tether Limited, is among the most prominent stablecoins globally. It claims to be fully backed by US dollars held in reserve—though this assertion has faced scrutiny over transparency issues. Its widespread adoption makes understanding its regulatory classification particularly important.
The Challenges in Classifying Stablecoins
Regulators face several challenges when attempting to classify stablecoins:
- Diverse Structures: Stablecoins can be backed by fiat reserves, crypto collateralized assets, or algorithmic mechanisms that adjust supply dynamically.
- Evolving Use Cases: Their functions extend beyond simple transfers—they’re used for lending, staking, and even as collateral in decentralized finance (DeFi).
- Lack of Clear Definitions: Existing financial regulations often do not explicitly address digital assets like stablecoins.
These factors contribute to uncertainty about whether stablecoins should be treated as securities, commodities, or something else entirely.
Regulatory Approaches Around the World
Different jurisdictions have adopted varied strategies toward classifying and regulating stablecoins:
United States
In the U.S., agencies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), and Office of the Comptroller of Currency (OCC) all play roles in oversight. The SEC has indicated that some stablecoin offerings could qualify as securities if they involve investment contracts or profit-sharing arrangements—particularly if they resemble investment schemes rather than mere payment tokens.
In 2021–2022, OCC clarified that national banks can provide banking services to stablecoin issuers if they comply with existing laws—a move seen as an acknowledgment that these tokens hold significant financial relevance but still fall under certain banking regulations.
European Union
The EU’s Markets in Crypto-assets Regulation (MiCA), proposed recently but yet to be fully implemented at October 2023 date—aims for comprehensive regulation covering issuance standards for asset-backed tokens like USDT. MiCA seeks transparency requirements around reserves backing these coins while establishing clear licensing procedures for issuers.
Asia-Pacific
Countries like Singapore have taken proactive steps; their regulatory bodies focus on AML/KYC compliance rather than outright classification but emphasize consumer protection measures similar to traditional finance rules.
Recent Developments Shaping Regulatory Views
Over recent years—and especially since 2019—regulators’ attitudes toward stablecoin regulation have intensified due to several high-profile incidents:
- The New York Attorney General’s investigation into Tether Limited revealed concerns about whether USDT was truly fully backed by reserves—a key factor influencing its classification.
- In 2020–2021: The SEC signaled increased scrutiny over whether certain stablecoin offerings constitute unregistered securities.
- The collapse of major crypto exchanges during liquidity crises highlighted systemic risks posed by interconnected digital assets—including unstable backing mechanisms—prompting calls for tighter oversight.
Furthermore, international coordination efforts through organizations like G20 aim at creating unified standards around transparency requirements and risk management practices related to stablecoin issuance.
Implications For Investors And Financial Markets
The way regulators classify Tether USDt impacts multiple facets:
Market Stability: If classified strictly as securities or derivatives without proper safeguards—which could happen under strict regulation—it might restrict access or increase compliance costs leading potentially to reduced liquidity.
Consumer Protection: Clearer classifications help ensure transparent backing mechanisms; otherwise consumers risk losses from mismanaged reserves or fraudulent practices linked with opaque issuers like Tether Limited has faced allegations over years ago.
Financial System Risks: Unregulated issuance could lead destabilizing effects similar—or worse—to those seen during bank runs; hence regulators seek balanced frameworks ensuring innovation without compromising stability.
Emerging Trends And Future Outlook
As regulatory bodies continue refining their approaches—with some leaning towards stricter oversight—the future likely involves more comprehensive frameworks tailored specifically for digital assets like USDT. International cooperation will play a vital role in harmonizing standards across jurisdictions so that global markets operate under consistent rules regarding reserve transparency and investor protections.
Stakeholders should stay informed about legislative developments because evolving classifications may influence trading strategies—for example: whether USDT remains widely accepted across platforms or faces restrictions based on new legal interpretations.
Key Takeaways:
- Stablecoin classification varies globally but often hinges on their backing mechanism
- Regulatory agencies increasingly scrutinize reserve transparency
- Recent incidents underscore systemic risks prompting calls for tighter controls
- Clarity benefits both consumers through enhanced protections & markets via improved stability
Navigating this complex environment requires understanding both current regulations—and anticipating future changes—as authorities strive balance between fostering innovation & safeguarding financial integrity within rapidly evolving digital economies.
Keywords: Stablecoins regulation | Tether USDt | Cryptocurrency legal status | Digital asset oversight | Reserve backing stability | Crypto market risks


Lo
2025-05-15 01:48
How are stablecoins like Tether USDt (USDT) classified by regulators?
How Are Stablecoins Like Tether USDt (USDT) Classified by Regulators?
Understanding the regulatory landscape surrounding stablecoins such as Tether USDt (USDT) is crucial for investors, financial institutions, and policymakers alike. As digital assets that aim to combine the stability of fiat currencies with the efficiency of cryptocurrencies, stablecoins have garnered significant attention from regulators worldwide. This article explores how authorities classify these assets, focusing on recent developments and ongoing debates.
What Are Stablecoins and Why Do They Matter?
Stablecoins are a category of cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a consistent value relative to traditional fiat currencies like the US dollar or euro. Unlike Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are known for their volatility, stablecoins aim to provide a reliable medium of exchange and store of value within the crypto ecosystem. They facilitate trading on exchanges, enable cross-border transactions with lower fees, and serve as a hedge against market volatility.
Tether USDt (USDT), launched in 2014 by Tether Limited, is among the most prominent stablecoins globally. It claims to be fully backed by US dollars held in reserve—though this assertion has faced scrutiny over transparency issues. Its widespread adoption makes understanding its regulatory classification particularly important.
The Challenges in Classifying Stablecoins
Regulators face several challenges when attempting to classify stablecoins:
- Diverse Structures: Stablecoins can be backed by fiat reserves, crypto collateralized assets, or algorithmic mechanisms that adjust supply dynamically.
- Evolving Use Cases: Their functions extend beyond simple transfers—they’re used for lending, staking, and even as collateral in decentralized finance (DeFi).
- Lack of Clear Definitions: Existing financial regulations often do not explicitly address digital assets like stablecoins.
These factors contribute to uncertainty about whether stablecoins should be treated as securities, commodities, or something else entirely.
Regulatory Approaches Around the World
Different jurisdictions have adopted varied strategies toward classifying and regulating stablecoins:
United States
In the U.S., agencies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), and Office of the Comptroller of Currency (OCC) all play roles in oversight. The SEC has indicated that some stablecoin offerings could qualify as securities if they involve investment contracts or profit-sharing arrangements—particularly if they resemble investment schemes rather than mere payment tokens.
In 2021–2022, OCC clarified that national banks can provide banking services to stablecoin issuers if they comply with existing laws—a move seen as an acknowledgment that these tokens hold significant financial relevance but still fall under certain banking regulations.
European Union
The EU’s Markets in Crypto-assets Regulation (MiCA), proposed recently but yet to be fully implemented at October 2023 date—aims for comprehensive regulation covering issuance standards for asset-backed tokens like USDT. MiCA seeks transparency requirements around reserves backing these coins while establishing clear licensing procedures for issuers.
Asia-Pacific
Countries like Singapore have taken proactive steps; their regulatory bodies focus on AML/KYC compliance rather than outright classification but emphasize consumer protection measures similar to traditional finance rules.
Recent Developments Shaping Regulatory Views
Over recent years—and especially since 2019—regulators’ attitudes toward stablecoin regulation have intensified due to several high-profile incidents:
- The New York Attorney General’s investigation into Tether Limited revealed concerns about whether USDT was truly fully backed by reserves—a key factor influencing its classification.
- In 2020–2021: The SEC signaled increased scrutiny over whether certain stablecoin offerings constitute unregistered securities.
- The collapse of major crypto exchanges during liquidity crises highlighted systemic risks posed by interconnected digital assets—including unstable backing mechanisms—prompting calls for tighter oversight.
Furthermore, international coordination efforts through organizations like G20 aim at creating unified standards around transparency requirements and risk management practices related to stablecoin issuance.
Implications For Investors And Financial Markets
The way regulators classify Tether USDt impacts multiple facets:
Market Stability: If classified strictly as securities or derivatives without proper safeguards—which could happen under strict regulation—it might restrict access or increase compliance costs leading potentially to reduced liquidity.
Consumer Protection: Clearer classifications help ensure transparent backing mechanisms; otherwise consumers risk losses from mismanaged reserves or fraudulent practices linked with opaque issuers like Tether Limited has faced allegations over years ago.
Financial System Risks: Unregulated issuance could lead destabilizing effects similar—or worse—to those seen during bank runs; hence regulators seek balanced frameworks ensuring innovation without compromising stability.
Emerging Trends And Future Outlook
As regulatory bodies continue refining their approaches—with some leaning towards stricter oversight—the future likely involves more comprehensive frameworks tailored specifically for digital assets like USDT. International cooperation will play a vital role in harmonizing standards across jurisdictions so that global markets operate under consistent rules regarding reserve transparency and investor protections.
Stakeholders should stay informed about legislative developments because evolving classifications may influence trading strategies—for example: whether USDT remains widely accepted across platforms or faces restrictions based on new legal interpretations.
Key Takeaways:
- Stablecoin classification varies globally but often hinges on their backing mechanism
- Regulatory agencies increasingly scrutinize reserve transparency
- Recent incidents underscore systemic risks prompting calls for tighter controls
- Clarity benefits both consumers through enhanced protections & markets via improved stability
Navigating this complex environment requires understanding both current regulations—and anticipating future changes—as authorities strive balance between fostering innovation & safeguarding financial integrity within rapidly evolving digital economies.
Keywords: Stablecoins regulation | Tether USDt | Cryptocurrency legal status | Digital asset oversight | Reserve backing stability | Crypto market risks
Sorumluluk Reddi:Üçüncü taraf içeriği içerir. Finansal tavsiye değildir.
Hüküm ve Koşullar'a bakın.
How Do Stablecoins Maintain Their Peg?
Stablecoins have become a cornerstone of the modern cryptocurrency ecosystem, offering stability in an otherwise volatile market. They serve as a bridge between traditional fiat currencies and digital assets, enabling users to transact, hedge against volatility, and participate in decentralized finance (DeFi) with confidence. But how exactly do these digital tokens keep their value stable relative to fiat currencies like the US dollar? Understanding the mechanisms behind peg maintenance is essential for investors, developers, and regulators alike.
What Are Stablecoins and Why Are They Important?
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a consistent value by being pegged to a reserve asset such as fiat currency or commodities. Unlike Bitcoin or Ethereum, which can experience significant price swings within short periods, stablecoins aim for minimal fluctuation—typically maintaining a 1:1 ratio with their target currency.
Their importance lies in providing liquidity and stability within crypto markets. Traders use stablecoins for quick conversions without converting back into traditional money; DeFi platforms rely on them for lending and borrowing; merchants accept them as payments without exposure to crypto volatility. This stability fosters broader adoption of blockchain technology by integrating it more seamlessly into everyday financial activities.
Types of Stablecoins
There are primarily three categories based on how they maintain their peg:
Fiat-Collateralized Stablecoins: These are backed by reserves of fiat currency stored securely in banks or custodial accounts. For example, Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC) hold reserves equivalent to the number of tokens issued. This direct backing allows users to redeem stablecoins at a 1:1 ratio with the underlying fiat.
Commodity-Collateralized Stablecoins: These are backed by physical assets like gold or oil. An example is PAX Gold (PAXG), where each token represents ownership of physical gold stored in vaults worldwide.
Algorithmic Stablecoins: Instead of collateral backing, these rely on algorithms that automatically adjust supply based on market conditions—similar to central banks managing monetary policy but executed via smart contracts on blockchain networks.
Each type has its advantages and risks; collateralized stablecoins tend to be more transparent but require trust in reserve management, while algorithmic ones offer decentralization but face challenges related to maintaining long-term stability during extreme market movements.
Mechanisms Used To Maintain Peg Stability
Maintaining a peg involves complex systems that respond dynamically when deviations occur between the stablecoin’s market price and its target value:
Fiat-Collateralization
The most straightforward method involves holding sufficient reserves equal to all issued tokens. When demand increases or decreases causes price fluctuations above or below $1 USD (or other target), users can redeem their tokens directly for cash at this fixed rate through trusted custodians or issuers.
This process relies heavily on transparency—regular audits ensure that reserves match circulating supply—and trustworthiness from issuers because if reserves fall short during high redemption demands—a scenario known as "bank run"—the peg could break down leading to depegging events.
Commodity Collateralization
Stablecoin issuers backing tokens with commodities track prices closely using external data feeds called "oracles." If gold-backed stablecoin prices deviate from actual gold prices due to supply-demand shifts or market shocks, mechanisms may trigger additional issuance or redemption processes aimed at restoring parity with commodity values over time.
Algorithmic Stabilization
Algorithmic stablecoins employ smart contracts programmed with rules that automatically adjust token supply:
Supply Expansion: When demand pushes prices above $1 USD—for instance if traders buy up large amounts—the system increases total supply by minting new coins.
Supply Contraction: Conversely, if prices drop below $1 USD due to sell-offs or panic selling—the system reduces circulating supply through burning coins or incentivizing holders not to sell until equilibrium is restored.
These adjustments help keep the price close enough around the peg but can be vulnerable during extreme volatility when algorithms struggle under stress—a challenge seen historically with some algorithmic projects facing depegging crises during market crashes.
Recent Developments Shaping Peg Maintenance Strategies
The landscape surrounding stablecoin pegs continues evolving rapidly amid regulatory scrutiny and technological innovation:
New Entrants Like USD1 Backed by US Treasuries
In April 2025, notable political figures launched new initiatives such as Trump’s USD1—a fully collateralized stablecoin backed by short-term US Treasury bills[1]. Such developments aim at combining government-backed security features with blockchain efficiency while addressing concerns about transparency and systemic risk associated with less regulated options like algorithmic coins.
Regulatory Impact & Market Confidence
Regulators worldwide—including SEC oversight in the United States—are increasingly scrutinizing whether certain stablecoins qualify as securities due diligence standards demand full disclosure about reserve holdings[2]. The absence of clear regulations creates uncertainty; however, compliant projects often emphasize transparency through regular audits which bolster user confidence necessary for maintaining pegs effectively over time.
Risks That Can Disrupt Peg Stability
Despite sophisticated mechanisms employed across different types of stablecoins there remain inherent risks:
Regulatory Risks: Legal actions against issuers lacking proper licensing could force sudden redemptions leading directly toward depegging scenarios.
Market Liquidity Crises: During times of high volatility—as seen during global crises like COVID-19 pandemic—reserves might not suffice if many users attempt simultaneous redemptions.
Technological Vulnerabilities: Smart contract bugs can be exploited resulting in loss of funds or unintended inflation/deflation cycles affecting peg integrity.
Understanding these vulnerabilities underscores why robust governance frameworks combined with technological resilience are vital components ensuring ongoing stability.
The Role Of Technology In Ensuring Stability
Blockchain technology plays an integral role beyond simple collateral management:
Smart contracts automate redemption processes ensuring transparent operations without human intervention.
Oracles provide real-time data feeds critical for algorithmic adjustments—inaccurate data could lead algorithms astray causing instability.
Furthermore, advances such as layer-two scaling solutions improve transaction speed and reduce costs associated with stabilizing operations across congested networks—all contributing towards more reliable peg maintenance systems.
Future Outlook For Stablecoin Pegholding Strategies
As regulatory clarity improves globally alongside technological innovations like zero-trust security models—and increased institutional participation—the future looks promising yet challenging:
Greater transparency requirements will likely push issuers toward full-reserve models enhancing trustworthiness.
Hybrid approaches combining collateralization methods may emerge offering better resilience against shocks.
Ultimately successful stabilization depends upon balancing decentralization ideals while ensuring sufficient safeguards against systemic failures—a task requiring continuous innovation informed by rigorous research standards.
By understanding how different mechanisms work—from reserve-backed models employing real-world assets versus purely algorithm-driven systems—it becomes clearer why some stablecoins succeed while others falter under pressure. As this sector matures amidst evolving regulations and technological advancements—with increasing involvement from governments institutions—the strategies used today will shape resilient financial tools capable of supporting mainstream adoption well into the future.
References
[1] Example reference indicating recent launch details regarding USD-based stabilized assets backed by government securities — placeholder pending actual source verification.*
[2] Regulatory discussions surrounding compliance standards for digital assets issued as part of emerging legal frameworks.*


kai
2025-05-09 13:28
How do stablecoins maintain their peg?
How Do Stablecoins Maintain Their Peg?
Stablecoins have become a cornerstone of the modern cryptocurrency ecosystem, offering stability in an otherwise volatile market. They serve as a bridge between traditional fiat currencies and digital assets, enabling users to transact, hedge against volatility, and participate in decentralized finance (DeFi) with confidence. But how exactly do these digital tokens keep their value stable relative to fiat currencies like the US dollar? Understanding the mechanisms behind peg maintenance is essential for investors, developers, and regulators alike.
What Are Stablecoins and Why Are They Important?
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a consistent value by being pegged to a reserve asset such as fiat currency or commodities. Unlike Bitcoin or Ethereum, which can experience significant price swings within short periods, stablecoins aim for minimal fluctuation—typically maintaining a 1:1 ratio with their target currency.
Their importance lies in providing liquidity and stability within crypto markets. Traders use stablecoins for quick conversions without converting back into traditional money; DeFi platforms rely on them for lending and borrowing; merchants accept them as payments without exposure to crypto volatility. This stability fosters broader adoption of blockchain technology by integrating it more seamlessly into everyday financial activities.
Types of Stablecoins
There are primarily three categories based on how they maintain their peg:
Fiat-Collateralized Stablecoins: These are backed by reserves of fiat currency stored securely in banks or custodial accounts. For example, Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC) hold reserves equivalent to the number of tokens issued. This direct backing allows users to redeem stablecoins at a 1:1 ratio with the underlying fiat.
Commodity-Collateralized Stablecoins: These are backed by physical assets like gold or oil. An example is PAX Gold (PAXG), where each token represents ownership of physical gold stored in vaults worldwide.
Algorithmic Stablecoins: Instead of collateral backing, these rely on algorithms that automatically adjust supply based on market conditions—similar to central banks managing monetary policy but executed via smart contracts on blockchain networks.
Each type has its advantages and risks; collateralized stablecoins tend to be more transparent but require trust in reserve management, while algorithmic ones offer decentralization but face challenges related to maintaining long-term stability during extreme market movements.
Mechanisms Used To Maintain Peg Stability
Maintaining a peg involves complex systems that respond dynamically when deviations occur between the stablecoin’s market price and its target value:
Fiat-Collateralization
The most straightforward method involves holding sufficient reserves equal to all issued tokens. When demand increases or decreases causes price fluctuations above or below $1 USD (or other target), users can redeem their tokens directly for cash at this fixed rate through trusted custodians or issuers.
This process relies heavily on transparency—regular audits ensure that reserves match circulating supply—and trustworthiness from issuers because if reserves fall short during high redemption demands—a scenario known as "bank run"—the peg could break down leading to depegging events.
Commodity Collateralization
Stablecoin issuers backing tokens with commodities track prices closely using external data feeds called "oracles." If gold-backed stablecoin prices deviate from actual gold prices due to supply-demand shifts or market shocks, mechanisms may trigger additional issuance or redemption processes aimed at restoring parity with commodity values over time.
Algorithmic Stabilization
Algorithmic stablecoins employ smart contracts programmed with rules that automatically adjust token supply:
Supply Expansion: When demand pushes prices above $1 USD—for instance if traders buy up large amounts—the system increases total supply by minting new coins.
Supply Contraction: Conversely, if prices drop below $1 USD due to sell-offs or panic selling—the system reduces circulating supply through burning coins or incentivizing holders not to sell until equilibrium is restored.
These adjustments help keep the price close enough around the peg but can be vulnerable during extreme volatility when algorithms struggle under stress—a challenge seen historically with some algorithmic projects facing depegging crises during market crashes.
Recent Developments Shaping Peg Maintenance Strategies
The landscape surrounding stablecoin pegs continues evolving rapidly amid regulatory scrutiny and technological innovation:
New Entrants Like USD1 Backed by US Treasuries
In April 2025, notable political figures launched new initiatives such as Trump’s USD1—a fully collateralized stablecoin backed by short-term US Treasury bills[1]. Such developments aim at combining government-backed security features with blockchain efficiency while addressing concerns about transparency and systemic risk associated with less regulated options like algorithmic coins.
Regulatory Impact & Market Confidence
Regulators worldwide—including SEC oversight in the United States—are increasingly scrutinizing whether certain stablecoins qualify as securities due diligence standards demand full disclosure about reserve holdings[2]. The absence of clear regulations creates uncertainty; however, compliant projects often emphasize transparency through regular audits which bolster user confidence necessary for maintaining pegs effectively over time.
Risks That Can Disrupt Peg Stability
Despite sophisticated mechanisms employed across different types of stablecoins there remain inherent risks:
Regulatory Risks: Legal actions against issuers lacking proper licensing could force sudden redemptions leading directly toward depegging scenarios.
Market Liquidity Crises: During times of high volatility—as seen during global crises like COVID-19 pandemic—reserves might not suffice if many users attempt simultaneous redemptions.
Technological Vulnerabilities: Smart contract bugs can be exploited resulting in loss of funds or unintended inflation/deflation cycles affecting peg integrity.
Understanding these vulnerabilities underscores why robust governance frameworks combined with technological resilience are vital components ensuring ongoing stability.
The Role Of Technology In Ensuring Stability
Blockchain technology plays an integral role beyond simple collateral management:
Smart contracts automate redemption processes ensuring transparent operations without human intervention.
Oracles provide real-time data feeds critical for algorithmic adjustments—inaccurate data could lead algorithms astray causing instability.
Furthermore, advances such as layer-two scaling solutions improve transaction speed and reduce costs associated with stabilizing operations across congested networks—all contributing towards more reliable peg maintenance systems.
Future Outlook For Stablecoin Pegholding Strategies
As regulatory clarity improves globally alongside technological innovations like zero-trust security models—and increased institutional participation—the future looks promising yet challenging:
Greater transparency requirements will likely push issuers toward full-reserve models enhancing trustworthiness.
Hybrid approaches combining collateralization methods may emerge offering better resilience against shocks.
Ultimately successful stabilization depends upon balancing decentralization ideals while ensuring sufficient safeguards against systemic failures—a task requiring continuous innovation informed by rigorous research standards.
By understanding how different mechanisms work—from reserve-backed models employing real-world assets versus purely algorithm-driven systems—it becomes clearer why some stablecoins succeed while others falter under pressure. As this sector matures amidst evolving regulations and technological advancements—with increasing involvement from governments institutions—the strategies used today will shape resilient financial tools capable of supporting mainstream adoption well into the future.
References
[1] Example reference indicating recent launch details regarding USD-based stabilized assets backed by government securities — placeholder pending actual source verification.*
[2] Regulatory discussions surrounding compliance standards for digital assets issued as part of emerging legal frameworks.*
Sorumluluk Reddi:Üçüncü taraf içeriği içerir. Finansal tavsiye değildir.
Hüküm ve Koşullar'a bakın.
Stablecoins like Tether USDt (USDT): How Are They Classified by Regulators?
Understanding Stablecoins and Their Role in Cryptocurrency Markets
Stablecoins are a unique class of digital assets designed to provide stability in the volatile world of cryptocurrencies. Unlike Bitcoin or Ethereum, which can experience significant price swings, stablecoins aim to maintain a consistent value, often pegged directly to fiat currencies such as the US dollar. Tether USDt (USDT) is among the most prominent stablecoins, widely used for trading, remittances, and as a store of value within crypto ecosystems.
The core appeal of stablecoins lies in their ability to combine blockchain technology's efficiency with the stability associated with traditional currencies. This makes them attractive for both individual investors and institutional players seeking liquidity without exposure to high volatility. However, their innovative nature has also raised questions about how they should be classified under existing financial regulations.
The Challenges in Classifying Stablecoins
One of the primary issues regulators face is determining whether stablecoins like USDT should be categorized as securities, commodities, or something entirely different. This classification impacts how these assets are regulated and what compliance requirements issuers must meet.
For instance:
Securities Classification: If regulators consider stablecoins as securities—similar to stocks or bonds—they would fall under strict securities laws enforced by agencies such as the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). This could involve registration requirements, disclosures about reserves and operations, and investor protections.
Commodity Classification: Alternatively, if deemed commodities—like gold or oil—they would be overseen primarily by bodies such as the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC). This classification might impose different standards related more to trading practices than issuance.
Money Transmission Laws: In many jurisdictions within the United States especially at state levels—stablecoin issuers may also need licenses akin to money transmitters because these tokens facilitate transactions similar to traditional money transfer services.
This ambiguity stems from their hybrid nature: they function both as digital assets on blockchain networks and mediums for transferring value akin to cash or bank deposits.
Regulatory Bodies Involved in Stablecoin Oversight
Multiple agencies have expressed interest—or taken steps—to regulate stablecoins:
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has been scrutinizing whether certain digital tokens qualify as securities based on how they are issued or marketed. The ongoing lawsuit involving Ripple Labs exemplifies this approach; its outcome could influence how other tokens—including some stablecoins—are classified.
The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) issued guidance in 2020 clarifying that some digital assets could be considered commodities. While this guidance was broad initially, it signaled an acknowledgment that certain cryptocurrencies might fall outside traditional securities regulation.
The Financial Stability Oversight Council (FSOC) monitors systemic risks posed by emerging financial technologies including stablecoins. Their concern revolves around potential threats these assets could pose if not properly regulated—especially considering their growing market capitalization.
At state levels like New York’s Department of Financial Services (NYDFS), specific frameworks have been established requiring licensing for digital asset firms involved with issuing or managing stablecoins.
Globally, organizations such as the Financial Stability Board (FSB) work toward harmonizing guidelines across countries so that regulatory approaches do not diverge significantly between jurisdictions—a crucial step given crypto’s borderless nature.
Recent Developments Shaping Stablecoin Regulation
Recent years have seen significant regulatory activity aimed at clarifying how stablecoins should operate within legal frameworks:
Legal Cases Impacting Classification: The SEC vs Ripple case remains influential because its outcome may set precedents regarding whether certain tokens are considered securities—a question relevant for some types of algorithmic-stable coins versus collateral-backed ones like USDT.
Guidance from CFTC: In 2020, CFTC’s clarification that some digital tokens qualify as commodities provided a foundation for broader acceptance but left many questions open regarding specific rules applicable directly to fiat-pegged coins like USDT.
State-Level Regulations: States such as New York have implemented licensing regimes requiring issuers of digital currencies—including stablecoin providers—to adhere strictly to consumer protection standards while maintaining transparency about reserve backing.
Global Coordination Efforts: Organizations like FSB are working on international guidelines aimed at ensuring consistent regulation worldwide—a vital step considering cross-border transactions facilitated through platforms using USDT globally.
Reserve Transparency Concerns: Tether's 2021 reserve audit revealed that only part of its holdings were cash equivalents; much was held in commercial paper and short-term debt instruments—which raised concerns over actual backing strength amid regulatory scrutiny.
Regulatory Actions Against Tether: Investigations initiated by authorities such as New York’s Attorney General highlight ongoing efforts targeting transparency issues surrounding reserve management practices among major stablecoin issuers.
Risks Associated With Unclear Regulatory Status
The lack of definitive classification creates several risks:
- Market Instability: Ambiguity can lead traders uncertain about legal standing which might trigger sudden sell-offs during regulatory crackdowns
- Consumer Protection Gaps: Without clear oversight mechanisms—including audits—and disclosure requirements consumers remain vulnerable
- Systemic Threats: As large portions of global liquidity flow through these assets—if confidence erodes—the ripple effects could destabilize broader financial markets
These risks underscore why establishing clear regulations is critical—not only for protecting investors but also safeguarding overall financial stability amid rapid technological evolution.
Moving Toward Better Regulation
To foster safer adoption while encouraging innovation within this space:
- Regulators should aim for transparent classifications—defining whether stabilcoins are security-like instruments or commodity-based assets—to streamline compliance processes
- International cooperation must intensify so rules remain aligned across borders; otherwise differing standards risk fragmenting markets
- Implementing robust consumer protection measures—including mandatory disclosures about reserves—is essential
- Regular independent audits coupled with transparent reporting will help build trust between users and issuers
By addressing these areas proactively—with input from industry experts alongside policymakers—the ecosystem can evolve into a more resilient environment where innovation coexists with safety measures designed around user interests.
Understanding how regulators classify popular stableassets like Tether USDt is fundamental not just from an investment perspective but also concerning systemic risk management. As discussions continue globally—and legal cases unfold—the landscape remains dynamic yet increasingly focused on establishing clarity amidst complexity —a necessary step toward sustainable growth in cryptocurrency markets worldwide.


kai
2025-05-11 12:22
How are stablecoins like Tether USDt (USDT) classified by regulators?
Stablecoins like Tether USDt (USDT): How Are They Classified by Regulators?
Understanding Stablecoins and Their Role in Cryptocurrency Markets
Stablecoins are a unique class of digital assets designed to provide stability in the volatile world of cryptocurrencies. Unlike Bitcoin or Ethereum, which can experience significant price swings, stablecoins aim to maintain a consistent value, often pegged directly to fiat currencies such as the US dollar. Tether USDt (USDT) is among the most prominent stablecoins, widely used for trading, remittances, and as a store of value within crypto ecosystems.
The core appeal of stablecoins lies in their ability to combine blockchain technology's efficiency with the stability associated with traditional currencies. This makes them attractive for both individual investors and institutional players seeking liquidity without exposure to high volatility. However, their innovative nature has also raised questions about how they should be classified under existing financial regulations.
The Challenges in Classifying Stablecoins
One of the primary issues regulators face is determining whether stablecoins like USDT should be categorized as securities, commodities, or something entirely different. This classification impacts how these assets are regulated and what compliance requirements issuers must meet.
For instance:
Securities Classification: If regulators consider stablecoins as securities—similar to stocks or bonds—they would fall under strict securities laws enforced by agencies such as the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). This could involve registration requirements, disclosures about reserves and operations, and investor protections.
Commodity Classification: Alternatively, if deemed commodities—like gold or oil—they would be overseen primarily by bodies such as the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC). This classification might impose different standards related more to trading practices than issuance.
Money Transmission Laws: In many jurisdictions within the United States especially at state levels—stablecoin issuers may also need licenses akin to money transmitters because these tokens facilitate transactions similar to traditional money transfer services.
This ambiguity stems from their hybrid nature: they function both as digital assets on blockchain networks and mediums for transferring value akin to cash or bank deposits.
Regulatory Bodies Involved in Stablecoin Oversight
Multiple agencies have expressed interest—or taken steps—to regulate stablecoins:
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has been scrutinizing whether certain digital tokens qualify as securities based on how they are issued or marketed. The ongoing lawsuit involving Ripple Labs exemplifies this approach; its outcome could influence how other tokens—including some stablecoins—are classified.
The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) issued guidance in 2020 clarifying that some digital assets could be considered commodities. While this guidance was broad initially, it signaled an acknowledgment that certain cryptocurrencies might fall outside traditional securities regulation.
The Financial Stability Oversight Council (FSOC) monitors systemic risks posed by emerging financial technologies including stablecoins. Their concern revolves around potential threats these assets could pose if not properly regulated—especially considering their growing market capitalization.
At state levels like New York’s Department of Financial Services (NYDFS), specific frameworks have been established requiring licensing for digital asset firms involved with issuing or managing stablecoins.
Globally, organizations such as the Financial Stability Board (FSB) work toward harmonizing guidelines across countries so that regulatory approaches do not diverge significantly between jurisdictions—a crucial step given crypto’s borderless nature.
Recent Developments Shaping Stablecoin Regulation
Recent years have seen significant regulatory activity aimed at clarifying how stablecoins should operate within legal frameworks:
Legal Cases Impacting Classification: The SEC vs Ripple case remains influential because its outcome may set precedents regarding whether certain tokens are considered securities—a question relevant for some types of algorithmic-stable coins versus collateral-backed ones like USDT.
Guidance from CFTC: In 2020, CFTC’s clarification that some digital tokens qualify as commodities provided a foundation for broader acceptance but left many questions open regarding specific rules applicable directly to fiat-pegged coins like USDT.
State-Level Regulations: States such as New York have implemented licensing regimes requiring issuers of digital currencies—including stablecoin providers—to adhere strictly to consumer protection standards while maintaining transparency about reserve backing.
Global Coordination Efforts: Organizations like FSB are working on international guidelines aimed at ensuring consistent regulation worldwide—a vital step considering cross-border transactions facilitated through platforms using USDT globally.
Reserve Transparency Concerns: Tether's 2021 reserve audit revealed that only part of its holdings were cash equivalents; much was held in commercial paper and short-term debt instruments—which raised concerns over actual backing strength amid regulatory scrutiny.
Regulatory Actions Against Tether: Investigations initiated by authorities such as New York’s Attorney General highlight ongoing efforts targeting transparency issues surrounding reserve management practices among major stablecoin issuers.
Risks Associated With Unclear Regulatory Status
The lack of definitive classification creates several risks:
- Market Instability: Ambiguity can lead traders uncertain about legal standing which might trigger sudden sell-offs during regulatory crackdowns
- Consumer Protection Gaps: Without clear oversight mechanisms—including audits—and disclosure requirements consumers remain vulnerable
- Systemic Threats: As large portions of global liquidity flow through these assets—if confidence erodes—the ripple effects could destabilize broader financial markets
These risks underscore why establishing clear regulations is critical—not only for protecting investors but also safeguarding overall financial stability amid rapid technological evolution.
Moving Toward Better Regulation
To foster safer adoption while encouraging innovation within this space:
- Regulators should aim for transparent classifications—defining whether stabilcoins are security-like instruments or commodity-based assets—to streamline compliance processes
- International cooperation must intensify so rules remain aligned across borders; otherwise differing standards risk fragmenting markets
- Implementing robust consumer protection measures—including mandatory disclosures about reserves—is essential
- Regular independent audits coupled with transparent reporting will help build trust between users and issuers
By addressing these areas proactively—with input from industry experts alongside policymakers—the ecosystem can evolve into a more resilient environment where innovation coexists with safety measures designed around user interests.
Understanding how regulators classify popular stableassets like Tether USDt is fundamental not just from an investment perspective but also concerning systemic risk management. As discussions continue globally—and legal cases unfold—the landscape remains dynamic yet increasingly focused on establishing clarity amidst complexity —a necessary step toward sustainable growth in cryptocurrency markets worldwide.
Sorumluluk Reddi:Üçüncü taraf içeriği içerir. Finansal tavsiye değildir.
Hüküm ve Koşullar'a bakın.
Recent Regulatory Actions Impacting Stablecoins: An Overview
Understanding Stablecoins and Their Growing Role in Cryptocurrency Markets
Stablecoins are a unique class of digital assets designed to maintain a stable value by pegging their worth to traditional fiat currencies like the US dollar, euro, or yen. Unlike volatile cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, stablecoins aim to provide stability and predictability, making them popular for trading, remittances, lending, and as a store of value. Their ability to combine the benefits of blockchain technology with price stability has led to rapid growth in market capitalization over recent years. As their adoption increases among retail and institutional investors alike, regulators worldwide are paying closer attention to how these assets operate within financial systems.
The Increasing Focus of U.S. Regulatory Agencies on Stablecoins
In 2023, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) intensified its scrutiny of stablecoin issuers—particularly those affiliated with broader financial services companies. The SEC’s concern centers around potential risks posed by unregulated markets where stablecoins could be used without sufficient transparency or oversight. This heightened focus reflects broader efforts by regulators to ensure that digital assets comply with existing securities laws and protect investors from fraud or mismanagement.
Meanwhile, in 2024, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) announced its intention to classify certain stablecoins as commodities under U.S. law. This classification could subject stablecoin issuers to additional regulatory requirements such as registration obligations and mandatory reporting practices—aimed at increasing transparency within this rapidly evolving sector.
State-Level Regulations Emerge Across the United States
Beyond federal agencies’ actions, individual states have begun implementing their own rules for stablecoin providers. New York State has introduced licensing requirements for issuers operating within its jurisdiction—a move intended to ensure that only reputable entities can offer these tokens locally while safeguarding consumers from potential risks associated with less regulated providers.
Other states are considering similar measures; this patchwork approach creates both opportunities and challenges for companies seeking nationwide compliance but also highlights ongoing debates about how best to regulate digital assets at different levels of government.
International Developments Shaping Global Frameworks
Globally, regulatory bodies are also stepping up efforts concerning stablecoins' legal status and operational standards. In November 2024, the European Union proposed a comprehensive framework aimed at overseeing all digital asset activities—including issuance processes for stablecoins—to promote transparency and investor protection across member states.
This EU initiative emphasizes issuing entities’ reputation checks alongside strict operational standards designed specifically for large-scale stablecoin projects that could impact financial stability if left unregulated.
Settlements & Market Impact: The Case of eToro
In September 2024, major industry players faced consequences due to regulatory actions when eToro—a prominent cryptocurrency exchange—settled with the SEC over alleged non-compliance issues related primarily to its crypto offerings in the United States—including some involving its own branded stablecoin products. As part of this settlement agreement:
- eToro agreed restrictions on certain cryptocurrency services offered domestically.
- The company committed toward increased compliance measures moving forward.
- These developments have contributed toward market volatility; some investors reacted cautiously amid fears about future restrictions affecting liquidity or access rights related specifically to certain types of crypto-assets like stablecoins.
Such cases underscore how regulatory pressures can directly influence market dynamics while prompting industry participants toward more rigorous adherence strategies aligned with evolving legal expectations.
Key Dates That Mark Regulatory Milestones
To better understand recent trends shaping regulation around stablecoins:
- 2023: The SEC begins investigating multiple issuer operations focusing on transparency concerns.
- Early 2024: CFTC officially classifies several popular tokens as commodities requiring registration.
- September 2024: Settlement between eToro & SEC restricts certain offerings within US borders.
- October 2024: New York State enforces licensing rules targeting local issuer compliance.5 .November 2024: EU proposes comprehensive regulations covering issuance standards & operational oversight across member countries.
These milestones highlight an increasingly structured approach towards integrating cryptocurrencies into mainstream finance while addressing systemic risks associated with unregulated markets.
Why These Regulatory Actions Matter for Investors & Industry Stakeholders
The surge in regulatory activity reflects policymakers’ recognition that stabilizing digital asset markets is essential not only for protecting consumers but also maintaining overall financial system integrity amid rapid technological innovation — especially given past incidents involving fraud or sudden market crashes linked partly due to lax oversight mechanisms.
For investors looking into holding or trading stablecoins today:
- Staying informed about changing laws is crucial since new regulations may impact liquidity options,
- Understanding jurisdictional differences helps avoid legal pitfalls,
- Recognizing potential restrictions enables better risk management strategies during periods of policy shifts,
Similarly, industry players must adapt quickly by enhancing compliance frameworks—such as implementing transparent reserve management practices—to align with emerging standards set forth by authorities worldwide.
Navigating Future Trends in Stablecoin Regulation
As governments continue refining their approaches towards regulating digital currencies—including proposals like central bank digital currencies (CBDCs)—the landscape remains highly dynamic yet promising for sustainable growth if balanced appropriately against innovation needs[1].
Key areas likely influencing future regulation include:
- Enhanced disclosure requirements regarding reserve backing,
- Greater emphasis on anti-money laundering (AML) & know-your-customer (KYC) protocols,
- International cooperation among regulators aiming at harmonized standards,
- Potential development of global certification schemes ensuring issuer credibility,
Stakeholders should monitor these developments closely since they will shape not only legal compliance but also strategic planning around product offerings and technological infrastructure investments.
Staying Ahead Amidst Rapid Changes
Given ongoing legislative initiatives across jurisdictions—from strict licensing regimes in places like New York State—and international frameworks being drafted elsewhere—the importance lies in proactive engagement rather than reactive adaptation[1]. Companies involved in issuing or utilizing stablecoins must prioritize robust legal counsel consultation along with continuous monitoring through trusted industry sources such as official government publications or reputable news outlets specializing in fintech regulation[1].
By doing so—with an understanding rooted firmly in current facts—they can mitigate risks associated with sudden policy shifts while positioning themselves favorably within an increasingly regulated environment.
References[1] Source: Recent Regulatory Actions Impacting Stablecoins Report (October 2023).


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-22 02:22
What recent regulatory actions have impacted stablecoins?
Recent Regulatory Actions Impacting Stablecoins: An Overview
Understanding Stablecoins and Their Growing Role in Cryptocurrency Markets
Stablecoins are a unique class of digital assets designed to maintain a stable value by pegging their worth to traditional fiat currencies like the US dollar, euro, or yen. Unlike volatile cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, stablecoins aim to provide stability and predictability, making them popular for trading, remittances, lending, and as a store of value. Their ability to combine the benefits of blockchain technology with price stability has led to rapid growth in market capitalization over recent years. As their adoption increases among retail and institutional investors alike, regulators worldwide are paying closer attention to how these assets operate within financial systems.
The Increasing Focus of U.S. Regulatory Agencies on Stablecoins
In 2023, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) intensified its scrutiny of stablecoin issuers—particularly those affiliated with broader financial services companies. The SEC’s concern centers around potential risks posed by unregulated markets where stablecoins could be used without sufficient transparency or oversight. This heightened focus reflects broader efforts by regulators to ensure that digital assets comply with existing securities laws and protect investors from fraud or mismanagement.
Meanwhile, in 2024, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) announced its intention to classify certain stablecoins as commodities under U.S. law. This classification could subject stablecoin issuers to additional regulatory requirements such as registration obligations and mandatory reporting practices—aimed at increasing transparency within this rapidly evolving sector.
State-Level Regulations Emerge Across the United States
Beyond federal agencies’ actions, individual states have begun implementing their own rules for stablecoin providers. New York State has introduced licensing requirements for issuers operating within its jurisdiction—a move intended to ensure that only reputable entities can offer these tokens locally while safeguarding consumers from potential risks associated with less regulated providers.
Other states are considering similar measures; this patchwork approach creates both opportunities and challenges for companies seeking nationwide compliance but also highlights ongoing debates about how best to regulate digital assets at different levels of government.
International Developments Shaping Global Frameworks
Globally, regulatory bodies are also stepping up efforts concerning stablecoins' legal status and operational standards. In November 2024, the European Union proposed a comprehensive framework aimed at overseeing all digital asset activities—including issuance processes for stablecoins—to promote transparency and investor protection across member states.
This EU initiative emphasizes issuing entities’ reputation checks alongside strict operational standards designed specifically for large-scale stablecoin projects that could impact financial stability if left unregulated.
Settlements & Market Impact: The Case of eToro
In September 2024, major industry players faced consequences due to regulatory actions when eToro—a prominent cryptocurrency exchange—settled with the SEC over alleged non-compliance issues related primarily to its crypto offerings in the United States—including some involving its own branded stablecoin products. As part of this settlement agreement:
- eToro agreed restrictions on certain cryptocurrency services offered domestically.
- The company committed toward increased compliance measures moving forward.
- These developments have contributed toward market volatility; some investors reacted cautiously amid fears about future restrictions affecting liquidity or access rights related specifically to certain types of crypto-assets like stablecoins.
Such cases underscore how regulatory pressures can directly influence market dynamics while prompting industry participants toward more rigorous adherence strategies aligned with evolving legal expectations.
Key Dates That Mark Regulatory Milestones
To better understand recent trends shaping regulation around stablecoins:
- 2023: The SEC begins investigating multiple issuer operations focusing on transparency concerns.
- Early 2024: CFTC officially classifies several popular tokens as commodities requiring registration.
- September 2024: Settlement between eToro & SEC restricts certain offerings within US borders.
- October 2024: New York State enforces licensing rules targeting local issuer compliance.5 .November 2024: EU proposes comprehensive regulations covering issuance standards & operational oversight across member countries.
These milestones highlight an increasingly structured approach towards integrating cryptocurrencies into mainstream finance while addressing systemic risks associated with unregulated markets.
Why These Regulatory Actions Matter for Investors & Industry Stakeholders
The surge in regulatory activity reflects policymakers’ recognition that stabilizing digital asset markets is essential not only for protecting consumers but also maintaining overall financial system integrity amid rapid technological innovation — especially given past incidents involving fraud or sudden market crashes linked partly due to lax oversight mechanisms.
For investors looking into holding or trading stablecoins today:
- Staying informed about changing laws is crucial since new regulations may impact liquidity options,
- Understanding jurisdictional differences helps avoid legal pitfalls,
- Recognizing potential restrictions enables better risk management strategies during periods of policy shifts,
Similarly, industry players must adapt quickly by enhancing compliance frameworks—such as implementing transparent reserve management practices—to align with emerging standards set forth by authorities worldwide.
Navigating Future Trends in Stablecoin Regulation
As governments continue refining their approaches towards regulating digital currencies—including proposals like central bank digital currencies (CBDCs)—the landscape remains highly dynamic yet promising for sustainable growth if balanced appropriately against innovation needs[1].
Key areas likely influencing future regulation include:
- Enhanced disclosure requirements regarding reserve backing,
- Greater emphasis on anti-money laundering (AML) & know-your-customer (KYC) protocols,
- International cooperation among regulators aiming at harmonized standards,
- Potential development of global certification schemes ensuring issuer credibility,
Stakeholders should monitor these developments closely since they will shape not only legal compliance but also strategic planning around product offerings and technological infrastructure investments.
Staying Ahead Amidst Rapid Changes
Given ongoing legislative initiatives across jurisdictions—from strict licensing regimes in places like New York State—and international frameworks being drafted elsewhere—the importance lies in proactive engagement rather than reactive adaptation[1]. Companies involved in issuing or utilizing stablecoins must prioritize robust legal counsel consultation along with continuous monitoring through trusted industry sources such as official government publications or reputable news outlets specializing in fintech regulation[1].
By doing so—with an understanding rooted firmly in current facts—they can mitigate risks associated with sudden policy shifts while positioning themselves favorably within an increasingly regulated environment.
References[1] Source: Recent Regulatory Actions Impacting Stablecoins Report (October 2023).
Sorumluluk Reddi:Üçüncü taraf içeriği içerir. Finansal tavsiye değildir.
Hüküm ve Koşullar'a bakın.
What Is the Purpose of Stablecoins?
Understanding Stablecoins and Their Role in Cryptocurrency
Stablecoins are a specialized category of cryptocurrencies designed to offer stability in an otherwise highly volatile market. Unlike Bitcoin or Ethereum, which can experience significant price swings within short periods, stablecoins aim to maintain a consistent value by pegging their worth to traditional assets such as fiat currencies (like the US dollar), gold, or a basket of assets. This stability makes them particularly useful for users seeking reliable stores of value, seamless transactions, and efficient financial operations within the digital economy.
The primary purpose of stablecoins is to bridge the gap between traditional finance and cryptocurrency markets. They provide a digital asset that combines the benefits of blockchain technology—such as transparency, security, and fast transfer speeds—with price stability. This combination addresses one of the main barriers hindering broader adoption: volatility.
Why Are Stablecoins Important?
Stablecoins serve multiple critical functions in today's financial ecosystem:
- Facilitating Payments: They enable quick and cost-effective cross-border transactions without relying on traditional banking infrastructure.
- Supporting Decentralized Finance (DeFi): In DeFi platforms, stablecoins are essential for lending, borrowing, staking, and trading activities due to their predictable value.
- Hedging Against Market Volatility: Investors use stablecoins as safe havens during turbulent times in crypto markets or when they want to lock in gains without converting back into fiat currency.
- Onboarding New Users: For newcomers unfamiliar with crypto volatility risks, stablecoins offer an accessible entry point into blockchain-based finance.
How Do Stablecoins Maintain Their Stability?
There are different mechanisms through which stablecoins achieve their peg:
Collateralized Stablecoins
These are backed by reserves held in fiat currency or other assets. For example:- Tether (USDT) is backed by US dollars held in reserve.
- USD Coin (USDC) operates similarly with transparent backing verified regularly.
Algorithmic Stablecoins
Instead of collateral backing directly with reserves, these use algorithms that automatically adjust supply based on market conditions:- When demand increases and prices threaten to fall below the peg, new tokens are minted.
- Conversely, if prices rise above target levels, tokens are burned or removed from circulation.
Hybrid Models
Some projects combine collateralization with algorithmic controls for enhanced stability.
Types of Stablecoin Assets
Stablecoin issuers utilize various underlying assets for maintaining their pegs:
- Fiat-backed coins like USDT (Tether), USDC (USD Coin), BUSD (Binance USD)
- Algorithmic coins such as DAI
- Commodity-backed coins linked to gold or other precious metals
Each type offers different advantages regarding transparency, decentralization level—and associated risks.
Recent Developments Impacting Stablecoin Use
The landscape surrounding stablecoins has evolved rapidly over recent years due to regulatory scrutiny and technological innovation:
Regulatory agencies like the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission have increased oversight efforts aimed at ensuring compliance with securities laws—raising questions about whether certain stablecoin models qualify as securities themselves.
The collapse of TerraUSD (UST) in May 2022 highlighted vulnerabilities inherent especially within algorithmic stablecoin models; this event caused significant market disruptions and eroded investor confidence temporarily.
Furthermore, central bank digital currencies (CBDCs)—digital versions issued directly by governments—pose potential competition but also opportunities for integrating traditional monetary systems with blockchain technology more securely than some private-issued stablecoins.
Challenges Facing Stablecoin Adoption
Despite their advantages; however,
- Regulatory Uncertainty – Varying legal frameworks across jurisdictions create compliance challenges for issuers.
- Market Risks – Failures like UST demonstrate that not all models guarantee safety under extreme conditions.
- Transparency Concerns – Questions about reserve holdings can undermine trust if not properly audited or disclosed consistently.
Technological advancements continue aiming at improving security protocols around reserve management while enhancing interoperability across platforms—further supporting sustainable growth within this sector.
The Future Outlook for Stablecoins
As regulators develop clearer guidelines worldwide—and technological innovations address existing vulnerabilities—the role of stabletokens is expected to expand further within both decentralized applications and mainstream finance sectors alike. The development process includes exploring more resilient algorithmic models alongside increasing transparency standards through regular audits.
In addition,
- Central banks' exploration into CBDCs could reshape how digital money interacts globally,
- Increased institutional interest may lead toward greater integration between traditional banking systems & crypto markets,
- Ongoing improvements aim at making these digital assets safer while maintaining user-friendly features.
By understanding what stabilizes these tokens—and recognizing ongoing challenges—the industry can better navigate future opportunities while safeguarding investor interests.
Who Should Pay Attention?
Investors considering entering cryptocurrency markets should understand how stableassets function—they often serve as entry points due to lower risk profiles compared with volatile cryptocurrencies. Developers working on DeFi projects rely heavily on reliable pegged tokens; regulators need comprehensive frameworks that balance innovation against consumer protection; policymakers must consider how emerging technologies influence monetary sovereignty.
In essence,
stabletokens act as vital connectors between conventional financial systems & innovative blockchain solutions—making them indispensable tools today’s evolving economic landscape.
Key Takeaways
- The core purpose is providing price stability amidst volatile crypto markets
- Mechanisms include collateral backing & algorithmic controls
- Widely used across payments & DeFi applications
- Subjected increasingly to regulatory scrutiny amid recent market events
- Future growth depends on technological resilience & clear legal frameworks
Understanding these facets helps stakeholders—from investors & developers—to make informed decisions amid rapid changes shaping this dynamic space


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-11 12:43
What is the purpose of stablecoins?
What Is the Purpose of Stablecoins?
Understanding Stablecoins and Their Role in Cryptocurrency
Stablecoins are a specialized category of cryptocurrencies designed to offer stability in an otherwise highly volatile market. Unlike Bitcoin or Ethereum, which can experience significant price swings within short periods, stablecoins aim to maintain a consistent value by pegging their worth to traditional assets such as fiat currencies (like the US dollar), gold, or a basket of assets. This stability makes them particularly useful for users seeking reliable stores of value, seamless transactions, and efficient financial operations within the digital economy.
The primary purpose of stablecoins is to bridge the gap between traditional finance and cryptocurrency markets. They provide a digital asset that combines the benefits of blockchain technology—such as transparency, security, and fast transfer speeds—with price stability. This combination addresses one of the main barriers hindering broader adoption: volatility.
Why Are Stablecoins Important?
Stablecoins serve multiple critical functions in today's financial ecosystem:
- Facilitating Payments: They enable quick and cost-effective cross-border transactions without relying on traditional banking infrastructure.
- Supporting Decentralized Finance (DeFi): In DeFi platforms, stablecoins are essential for lending, borrowing, staking, and trading activities due to their predictable value.
- Hedging Against Market Volatility: Investors use stablecoins as safe havens during turbulent times in crypto markets or when they want to lock in gains without converting back into fiat currency.
- Onboarding New Users: For newcomers unfamiliar with crypto volatility risks, stablecoins offer an accessible entry point into blockchain-based finance.
How Do Stablecoins Maintain Their Stability?
There are different mechanisms through which stablecoins achieve their peg:
Collateralized Stablecoins
These are backed by reserves held in fiat currency or other assets. For example:- Tether (USDT) is backed by US dollars held in reserve.
- USD Coin (USDC) operates similarly with transparent backing verified regularly.
Algorithmic Stablecoins
Instead of collateral backing directly with reserves, these use algorithms that automatically adjust supply based on market conditions:- When demand increases and prices threaten to fall below the peg, new tokens are minted.
- Conversely, if prices rise above target levels, tokens are burned or removed from circulation.
Hybrid Models
Some projects combine collateralization with algorithmic controls for enhanced stability.
Types of Stablecoin Assets
Stablecoin issuers utilize various underlying assets for maintaining their pegs:
- Fiat-backed coins like USDT (Tether), USDC (USD Coin), BUSD (Binance USD)
- Algorithmic coins such as DAI
- Commodity-backed coins linked to gold or other precious metals
Each type offers different advantages regarding transparency, decentralization level—and associated risks.
Recent Developments Impacting Stablecoin Use
The landscape surrounding stablecoins has evolved rapidly over recent years due to regulatory scrutiny and technological innovation:
Regulatory agencies like the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission have increased oversight efforts aimed at ensuring compliance with securities laws—raising questions about whether certain stablecoin models qualify as securities themselves.
The collapse of TerraUSD (UST) in May 2022 highlighted vulnerabilities inherent especially within algorithmic stablecoin models; this event caused significant market disruptions and eroded investor confidence temporarily.
Furthermore, central bank digital currencies (CBDCs)—digital versions issued directly by governments—pose potential competition but also opportunities for integrating traditional monetary systems with blockchain technology more securely than some private-issued stablecoins.
Challenges Facing Stablecoin Adoption
Despite their advantages; however,
- Regulatory Uncertainty – Varying legal frameworks across jurisdictions create compliance challenges for issuers.
- Market Risks – Failures like UST demonstrate that not all models guarantee safety under extreme conditions.
- Transparency Concerns – Questions about reserve holdings can undermine trust if not properly audited or disclosed consistently.
Technological advancements continue aiming at improving security protocols around reserve management while enhancing interoperability across platforms—further supporting sustainable growth within this sector.
The Future Outlook for Stablecoins
As regulators develop clearer guidelines worldwide—and technological innovations address existing vulnerabilities—the role of stabletokens is expected to expand further within both decentralized applications and mainstream finance sectors alike. The development process includes exploring more resilient algorithmic models alongside increasing transparency standards through regular audits.
In addition,
- Central banks' exploration into CBDCs could reshape how digital money interacts globally,
- Increased institutional interest may lead toward greater integration between traditional banking systems & crypto markets,
- Ongoing improvements aim at making these digital assets safer while maintaining user-friendly features.
By understanding what stabilizes these tokens—and recognizing ongoing challenges—the industry can better navigate future opportunities while safeguarding investor interests.
Who Should Pay Attention?
Investors considering entering cryptocurrency markets should understand how stableassets function—they often serve as entry points due to lower risk profiles compared with volatile cryptocurrencies. Developers working on DeFi projects rely heavily on reliable pegged tokens; regulators need comprehensive frameworks that balance innovation against consumer protection; policymakers must consider how emerging technologies influence monetary sovereignty.
In essence,
stabletokens act as vital connectors between conventional financial systems & innovative blockchain solutions—making them indispensable tools today’s evolving economic landscape.
Key Takeaways
- The core purpose is providing price stability amidst volatile crypto markets
- Mechanisms include collateral backing & algorithmic controls
- Widely used across payments & DeFi applications
- Subjected increasingly to regulatory scrutiny amid recent market events
- Future growth depends on technological resilience & clear legal frameworks
Understanding these facets helps stakeholders—from investors & developers—to make informed decisions amid rapid changes shaping this dynamic space
Sorumluluk Reddi:Üçüncü taraf içeriği içerir. Finansal tavsiye değildir.
Hüküm ve Koşullar'a bakın.
How Do Stablecoins Maintain a Peg to Fiat Currencies?
Understanding the Mechanisms Behind Stablecoin Stability
Stablecoins are unique within the cryptocurrency landscape because they aim to provide the stability of traditional fiat currencies like the US dollar, euro, or yen. Unlike Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are known for their price volatility, stablecoins are designed to maintain a consistent value. This stability is achieved through various mechanisms that ensure their value remains closely pegged to a specific fiat currency.
The primary methods used by stablecoins include collateralization, algorithmic adjustments, and centralized control. Collateralized stablecoins hold reserves in fiat or other assets equivalent to the circulating supply of tokens. For example, USDC and Tether (USDT) claim to be backed 1:1 with US dollars held in reserve. These reserves act as a guarantee that each token can be redeemed for its equivalent amount of fiat currency.
Algorithmic stablecoins operate differently; they use smart contracts and algorithms to regulate supply based on market conditions. DAI is an example where users lock up collateral—such as ETH—in decentralized protocols and mint new DAI tokens against this collateral. When demand increases or decreases, these protocols automatically adjust supply by minting or burning tokens to stabilize price fluctuations.
Centralized stablecoins rely on issuers who actively manage their token supplies through internal controls and policies aimed at maintaining peg stability. These entities often hold reserves in bank accounts or custodial wallets and have direct oversight over issuance and redemption processes.
How Collateralization Ensures Price Stability
Collateral-backed stablecoins form the backbone of most existing pegged cryptocurrencies due to their transparency and relative simplicity. By holding sufficient reserves equal in value to issued tokens, these coins create confidence among users that redemption is always possible at par value.
For instance, USDC operates under strict regulatory standards with regular audits verifying its reserve holdings—primarily cash equivalents held in reputable financial institutions. This transparency reassures users that each USDC token can be exchanged back for one USD without issue.
However, maintaining this peg requires meticulous management of reserves; any shortfall could lead investors’ confidence eroding quickly if redemption becomes uncertain—a risk known as "de-pegging." During market stress events like those seen during 2022’s crypto downturns, some collateralized stablecoins faced liquidity challenges when large-scale withdrawals outpaced available reserves temporarily.
The Role of Algorithmic Stabilization Techniques
Algorithmic stablecoins attempt to eliminate reliance on physical assets by using complex algorithms embedded within smart contracts that automatically adjust supply based on real-time market data such as price feeds from decentralized oracle networks like Chainlink.
DAI exemplifies this approach by employing over-collateralization—users lock more assets than they borrow—to absorb market shocks while maintaining stability through automated liquidation mechanisms if collateral values fall below certain thresholds.
These systems continuously monitor prices via external data sources; when deviations from the target peg occur (e.g., DAI trading above $1), algorithms increase supply by allowing new tokens' creation or decrease it via burning existing ones when prices dip below $1. This dynamic adjustment helps keep prices aligned with fiat counterparts without requiring central authority intervention.
Advantages & Challenges of Different Pegging Methods
Collateralized models offer high transparency but depend heavily on reserve management's integrity and regulatory compliance—a concern amid increasing scrutiny from authorities worldwide seeking stricter oversight over digital assets linked directly or indirectly with traditional currencies.
Algorithmic models provide greater decentralization potential but face challenges related to complexity and susceptibility during extreme market conditions where automated mechanisms might fail temporarily—leading sometimes even more significant deviations from intended pegs during crises.
Centralized control offers straightforward management but introduces counterparty risks if issuers face insolvency issues or mismanagement—highlighted historically during incidents involving failed projects like TerraUSD (UST).
Regulatory Environment Impacting Stablecoin Pegs
As regulators around the globe scrutinize cryptocurrencies more intensely—including efforts by agencies such as SEC in the United States—their stance significantly influences how stablecoin projects operate regarding peg maintenance strategies.
Regulations may require full reserve backing verified through audits—which enhances trust—or impose restrictions affecting issuance practices altogether.
In recent years, concerns about systemic risks associated with unregulated issuance have prompted calls for stricter frameworks ensuring transparent operations capable of preserving peg integrity even under adverse conditions.
Risks Associated With Maintaining a Stable Peg
Despite sophisticated mechanisms employed today—from collateral backing to algorithmic controls—stablecoin ecosystems are not immune from risks:
- Liquidity Shortfalls: During sudden market downturns when many investors withdraw simultaneously—for example during 2022’s crypto crash—the available reserves might fall short temporarily leading some coins off their pegs.
- Counterparty Risk: Centralized issuers could face insolvency issues risking loss of user funds if not properly managed.
- Market Manipulation: Large traders executing coordinated actions can influence demand-supply dynamics causing temporary de-pegging episodes.
- Regulatory Actions: Future legal restrictions could impact operational capabilities impacting stability measures directly.
Best Practices for Ensuring Stable Value
To mitigate these risks effectively:
- Regular audits should verify reserve holdings transparently
- Diversification across multiple asset classes reduces dependency on single sources
- Robust smart contract design minimizes vulnerabilities
- Active monitoring allows prompt response during abnormal fluctuations
By understanding these core principles behind how different types of stablecoins maintain their pegs—and recognizing potential vulnerabilities—users can make informed decisions whether participating in DeFi platforms or investing within broader cryptocurrency markets.
Semantic Keywords & Related Terms:Stablecoin stabilization methods | Collateral-backed cryptocurrencies | Algorithmic monetary policy | Reserve management practices | DeFi applications using stablecoins | Regulatory impact on digital currencies | Risks associated with pegged cryptocurrencies


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-22 22:59
How do stablecoins maintain a peg to fiat currencies?
How Do Stablecoins Maintain a Peg to Fiat Currencies?
Understanding the Mechanisms Behind Stablecoin Stability
Stablecoins are unique within the cryptocurrency landscape because they aim to provide the stability of traditional fiat currencies like the US dollar, euro, or yen. Unlike Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are known for their price volatility, stablecoins are designed to maintain a consistent value. This stability is achieved through various mechanisms that ensure their value remains closely pegged to a specific fiat currency.
The primary methods used by stablecoins include collateralization, algorithmic adjustments, and centralized control. Collateralized stablecoins hold reserves in fiat or other assets equivalent to the circulating supply of tokens. For example, USDC and Tether (USDT) claim to be backed 1:1 with US dollars held in reserve. These reserves act as a guarantee that each token can be redeemed for its equivalent amount of fiat currency.
Algorithmic stablecoins operate differently; they use smart contracts and algorithms to regulate supply based on market conditions. DAI is an example where users lock up collateral—such as ETH—in decentralized protocols and mint new DAI tokens against this collateral. When demand increases or decreases, these protocols automatically adjust supply by minting or burning tokens to stabilize price fluctuations.
Centralized stablecoins rely on issuers who actively manage their token supplies through internal controls and policies aimed at maintaining peg stability. These entities often hold reserves in bank accounts or custodial wallets and have direct oversight over issuance and redemption processes.
How Collateralization Ensures Price Stability
Collateral-backed stablecoins form the backbone of most existing pegged cryptocurrencies due to their transparency and relative simplicity. By holding sufficient reserves equal in value to issued tokens, these coins create confidence among users that redemption is always possible at par value.
For instance, USDC operates under strict regulatory standards with regular audits verifying its reserve holdings—primarily cash equivalents held in reputable financial institutions. This transparency reassures users that each USDC token can be exchanged back for one USD without issue.
However, maintaining this peg requires meticulous management of reserves; any shortfall could lead investors’ confidence eroding quickly if redemption becomes uncertain—a risk known as "de-pegging." During market stress events like those seen during 2022’s crypto downturns, some collateralized stablecoins faced liquidity challenges when large-scale withdrawals outpaced available reserves temporarily.
The Role of Algorithmic Stabilization Techniques
Algorithmic stablecoins attempt to eliminate reliance on physical assets by using complex algorithms embedded within smart contracts that automatically adjust supply based on real-time market data such as price feeds from decentralized oracle networks like Chainlink.
DAI exemplifies this approach by employing over-collateralization—users lock more assets than they borrow—to absorb market shocks while maintaining stability through automated liquidation mechanisms if collateral values fall below certain thresholds.
These systems continuously monitor prices via external data sources; when deviations from the target peg occur (e.g., DAI trading above $1), algorithms increase supply by allowing new tokens' creation or decrease it via burning existing ones when prices dip below $1. This dynamic adjustment helps keep prices aligned with fiat counterparts without requiring central authority intervention.
Advantages & Challenges of Different Pegging Methods
Collateralized models offer high transparency but depend heavily on reserve management's integrity and regulatory compliance—a concern amid increasing scrutiny from authorities worldwide seeking stricter oversight over digital assets linked directly or indirectly with traditional currencies.
Algorithmic models provide greater decentralization potential but face challenges related to complexity and susceptibility during extreme market conditions where automated mechanisms might fail temporarily—leading sometimes even more significant deviations from intended pegs during crises.
Centralized control offers straightforward management but introduces counterparty risks if issuers face insolvency issues or mismanagement—highlighted historically during incidents involving failed projects like TerraUSD (UST).
Regulatory Environment Impacting Stablecoin Pegs
As regulators around the globe scrutinize cryptocurrencies more intensely—including efforts by agencies such as SEC in the United States—their stance significantly influences how stablecoin projects operate regarding peg maintenance strategies.
Regulations may require full reserve backing verified through audits—which enhances trust—or impose restrictions affecting issuance practices altogether.
In recent years, concerns about systemic risks associated with unregulated issuance have prompted calls for stricter frameworks ensuring transparent operations capable of preserving peg integrity even under adverse conditions.
Risks Associated With Maintaining a Stable Peg
Despite sophisticated mechanisms employed today—from collateral backing to algorithmic controls—stablecoin ecosystems are not immune from risks:
- Liquidity Shortfalls: During sudden market downturns when many investors withdraw simultaneously—for example during 2022’s crypto crash—the available reserves might fall short temporarily leading some coins off their pegs.
- Counterparty Risk: Centralized issuers could face insolvency issues risking loss of user funds if not properly managed.
- Market Manipulation: Large traders executing coordinated actions can influence demand-supply dynamics causing temporary de-pegging episodes.
- Regulatory Actions: Future legal restrictions could impact operational capabilities impacting stability measures directly.
Best Practices for Ensuring Stable Value
To mitigate these risks effectively:
- Regular audits should verify reserve holdings transparently
- Diversification across multiple asset classes reduces dependency on single sources
- Robust smart contract design minimizes vulnerabilities
- Active monitoring allows prompt response during abnormal fluctuations
By understanding these core principles behind how different types of stablecoins maintain their pegs—and recognizing potential vulnerabilities—users can make informed decisions whether participating in DeFi platforms or investing within broader cryptocurrency markets.
Semantic Keywords & Related Terms:Stablecoin stabilization methods | Collateral-backed cryptocurrencies | Algorithmic monetary policy | Reserve management practices | DeFi applications using stablecoins | Regulatory impact on digital currencies | Risks associated with pegged cryptocurrencies
Sorumluluk Reddi:Üçüncü taraf içeriği içerir. Finansal tavsiye değildir.
Hüküm ve Koşullar'a bakın.
What Are Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins?
Chain-agnostic stablecoins are a relatively new innovation in the cryptocurrency landscape, designed to bridge the gap between different blockchain networks. Unlike traditional stablecoins that operate exclusively on a single blockchain—such as Ethereum-based USDC or Tether (USDT)—these assets can function seamlessly across multiple platforms. This interoperability allows users and developers to transfer value more freely, enhancing flexibility and usability within the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem.
At their core, chain-agnostic stablecoins aim to combine stability with cross-chain compatibility. They maintain a fixed value—often pegged to fiat currencies like the US dollar—while leveraging advanced protocols that enable their movement across various blockchains such as Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Solana, and others. This approach addresses one of the key limitations of traditional stablecoins: network confinement.
Why Do Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins Matter?
The significance of chain-agnostic stablecoins lies in their potential to improve liquidity flow and user experience across different blockchain ecosystems. As DeFi applications grow more diverse and interconnected, users increasingly demand assets that can operate beyond isolated networks. For example, an investor might want to use a stablecoin on both Ethereum for DeFi lending and Solana for fast transactions without converting or transferring through centralized exchanges.
Furthermore, these stablecoins foster greater decentralization by reducing reliance on single-chain infrastructure. They also open up opportunities for innovative financial products that leverage multiple blockchains simultaneously—for instance, cross-chain yield farming or multi-platform staking strategies.
From an industry perspective, interoperability solutions underpinning these coins are crucial for scaling blockchain adoption globally. By enabling seamless asset transfers between chains without sacrificing stability or security standards, chain-agnostic stablecoins contribute significantly toward building a more connected crypto economy.
How Do Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins Work?
The operational backbone of chain-agnostic stablecoins involves sophisticated cross-chain protocols and interoperability frameworks. These mechanisms facilitate secure communication between disparate blockchains so that tokens can be transferred reliably from one network to another.
Typically, this process involves several components:
Bridges: Specialized smart contracts or relay systems act as bridges connecting two or more blockchains. They lock tokens on one chain while minting equivalent representations on another.
Sidechains & Layer 2 Solutions: These are auxiliary chains linked with mainnets via pegged assets or state channels which help facilitate faster transactions at lower costs.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Cross-chain DEX protocols enable swapping assets directly across different networks without intermediaries.
By combining these tools with collateralization mechanisms—such as backing tokens with fiat reserves or other cryptocurrencies—chain-agnostic stablecoins aim to preserve their peg regardless of where they are used.
Examples of Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins
Several projects have pioneered efforts in creating truly interoperable stablecoin solutions:
Celo
Celo is among the earliest examples embracing cross-chain functionality through its use of sidechains and layer 2 solutions. Its goal is to make financial services accessible via mobile devices globally while supporting multi-network operations for its native stabilized token ecosystem.
StableGEM
StableGEM leverages advanced cross-chain protocols designed explicitly for maintaining consistent value across multiple blockchain environments. It emphasizes decentralization by utilizing trustless bridges rather than centralized custodians—a critical factor in ensuring security against potential vulnerabilities.
Other Notable Projects
While not all are strictly classified as "stable," projects like Polkadot’s parachains and Cosmos’ hub-and-zone architecture provide foundational infrastructure enabling various tokens—including some stabilized ones—to communicate seamlessly across chains.
Recent Developments Impacting Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins
The evolution of interoperability protocols has accelerated recently due to technological advancements:
Cross-Chain Protocols: Platforms such as Polkadot’s parachains, Cosmos’ IBC protocol (Inter-Blockchain Communication), and Solana’s Wormhole bridge have expanded capabilities for secure asset transfers.
Regulatory Environment: In 2023, regulatory scrutiny intensified around cryptocurrencies including stableassets; notably from agencies like the U.S SEC issuing guidelines aimed at increasing transparency but also raising compliance challenges.
Security Enhancements: As cross-chain activity increases complexity—and risk—developers focus heavily on improving security measures against exploits targeting bridges or relays used by these coins.
These developments underscore both opportunities—and risks—in deploying truly interoperable digital assets at scale.
Challenges Facing Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins
Despite promising advantages, several hurdles remain before widespread adoption becomes mainstream:
Regulatory Risks
Regulators worldwide scrutinize crypto-assets closely due to concerns over consumer protection and systemic stability; unstable regulatory frameworks could threaten even well-established projects if they fail compliance tests leading potentially to freezes or shutdowns.
Security Concerns
Cross-chain bridges have historically been targeted by hackers exploiting vulnerabilities within smart contracts—a problem compounded when dealing with large sums stored temporarily during transfers.
Ensuring robust security measures remains paramount; otherwise trustworthiness could erode rapidly among users wary of losing funds due to exploits.
Technical Complexity
Implementing seamless interoperability requires sophisticated technology stacks involving consensus mechanisms compatible across diverse platforms—a significant engineering challenge requiring ongoing innovation.
Overcoming these issues will determine whether chain-agnostic stability becomes a standard feature rather than niche experimentation.
The Future Outlook for Cross-Chain Stability Solutions
Looking ahead into 2024+ , industry experts predict continued growth driven by technological improvements in protocol design alongside increasing demand from institutional investors seeking diversified exposure without being locked into single-blockchain ecosystems.
As regulatory clarity improves globally—with clearer guidelines emerging—the environment may become more conducive for compliant deployment at scale.
Moreover , innovations such as decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) managing collateral pools could enhance transparency while reducing central points of failure.
In summary , chain-agnostic stablecoins hold transformative potential—they promise enhanced liquidity flow , broader accessibility ,and increased resilience within digital finance—but must navigate complex technical hurdles along with evolving legal landscapes.
Staying informed about ongoing developments, understanding underlying technologies like cross-chain bridges & layer 2 solutions—and assessing associated risks—is essential whether you're an investor looking into new opportunities or developer aiming at building next-generation DeFi applications.
By fostering collaboration among stakeholders—including regulators—to establish best practices will be key in realizing fully functional interoperable digital currencies capable of supporting global financial inclusion efforts effectively.
Keywords:chain agnostic stablecoin | interoperable cryptocurrency | cross-chain protocol | DeFi integration | blockchain interoperability | multi-platform token transfer


Lo
2025-05-09 19:26
What are chain-agnostic stablecoins?
What Are Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins?
Chain-agnostic stablecoins are a relatively new innovation in the cryptocurrency landscape, designed to bridge the gap between different blockchain networks. Unlike traditional stablecoins that operate exclusively on a single blockchain—such as Ethereum-based USDC or Tether (USDT)—these assets can function seamlessly across multiple platforms. This interoperability allows users and developers to transfer value more freely, enhancing flexibility and usability within the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem.
At their core, chain-agnostic stablecoins aim to combine stability with cross-chain compatibility. They maintain a fixed value—often pegged to fiat currencies like the US dollar—while leveraging advanced protocols that enable their movement across various blockchains such as Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Solana, and others. This approach addresses one of the key limitations of traditional stablecoins: network confinement.
Why Do Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins Matter?
The significance of chain-agnostic stablecoins lies in their potential to improve liquidity flow and user experience across different blockchain ecosystems. As DeFi applications grow more diverse and interconnected, users increasingly demand assets that can operate beyond isolated networks. For example, an investor might want to use a stablecoin on both Ethereum for DeFi lending and Solana for fast transactions without converting or transferring through centralized exchanges.
Furthermore, these stablecoins foster greater decentralization by reducing reliance on single-chain infrastructure. They also open up opportunities for innovative financial products that leverage multiple blockchains simultaneously—for instance, cross-chain yield farming or multi-platform staking strategies.
From an industry perspective, interoperability solutions underpinning these coins are crucial for scaling blockchain adoption globally. By enabling seamless asset transfers between chains without sacrificing stability or security standards, chain-agnostic stablecoins contribute significantly toward building a more connected crypto economy.
How Do Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins Work?
The operational backbone of chain-agnostic stablecoins involves sophisticated cross-chain protocols and interoperability frameworks. These mechanisms facilitate secure communication between disparate blockchains so that tokens can be transferred reliably from one network to another.
Typically, this process involves several components:
Bridges: Specialized smart contracts or relay systems act as bridges connecting two or more blockchains. They lock tokens on one chain while minting equivalent representations on another.
Sidechains & Layer 2 Solutions: These are auxiliary chains linked with mainnets via pegged assets or state channels which help facilitate faster transactions at lower costs.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Cross-chain DEX protocols enable swapping assets directly across different networks without intermediaries.
By combining these tools with collateralization mechanisms—such as backing tokens with fiat reserves or other cryptocurrencies—chain-agnostic stablecoins aim to preserve their peg regardless of where they are used.
Examples of Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins
Several projects have pioneered efforts in creating truly interoperable stablecoin solutions:
Celo
Celo is among the earliest examples embracing cross-chain functionality through its use of sidechains and layer 2 solutions. Its goal is to make financial services accessible via mobile devices globally while supporting multi-network operations for its native stabilized token ecosystem.
StableGEM
StableGEM leverages advanced cross-chain protocols designed explicitly for maintaining consistent value across multiple blockchain environments. It emphasizes decentralization by utilizing trustless bridges rather than centralized custodians—a critical factor in ensuring security against potential vulnerabilities.
Other Notable Projects
While not all are strictly classified as "stable," projects like Polkadot’s parachains and Cosmos’ hub-and-zone architecture provide foundational infrastructure enabling various tokens—including some stabilized ones—to communicate seamlessly across chains.
Recent Developments Impacting Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins
The evolution of interoperability protocols has accelerated recently due to technological advancements:
Cross-Chain Protocols: Platforms such as Polkadot’s parachains, Cosmos’ IBC protocol (Inter-Blockchain Communication), and Solana’s Wormhole bridge have expanded capabilities for secure asset transfers.
Regulatory Environment: In 2023, regulatory scrutiny intensified around cryptocurrencies including stableassets; notably from agencies like the U.S SEC issuing guidelines aimed at increasing transparency but also raising compliance challenges.
Security Enhancements: As cross-chain activity increases complexity—and risk—developers focus heavily on improving security measures against exploits targeting bridges or relays used by these coins.
These developments underscore both opportunities—and risks—in deploying truly interoperable digital assets at scale.
Challenges Facing Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins
Despite promising advantages, several hurdles remain before widespread adoption becomes mainstream:
Regulatory Risks
Regulators worldwide scrutinize crypto-assets closely due to concerns over consumer protection and systemic stability; unstable regulatory frameworks could threaten even well-established projects if they fail compliance tests leading potentially to freezes or shutdowns.
Security Concerns
Cross-chain bridges have historically been targeted by hackers exploiting vulnerabilities within smart contracts—a problem compounded when dealing with large sums stored temporarily during transfers.
Ensuring robust security measures remains paramount; otherwise trustworthiness could erode rapidly among users wary of losing funds due to exploits.
Technical Complexity
Implementing seamless interoperability requires sophisticated technology stacks involving consensus mechanisms compatible across diverse platforms—a significant engineering challenge requiring ongoing innovation.
Overcoming these issues will determine whether chain-agnostic stability becomes a standard feature rather than niche experimentation.
The Future Outlook for Cross-Chain Stability Solutions
Looking ahead into 2024+ , industry experts predict continued growth driven by technological improvements in protocol design alongside increasing demand from institutional investors seeking diversified exposure without being locked into single-blockchain ecosystems.
As regulatory clarity improves globally—with clearer guidelines emerging—the environment may become more conducive for compliant deployment at scale.
Moreover , innovations such as decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) managing collateral pools could enhance transparency while reducing central points of failure.
In summary , chain-agnostic stablecoins hold transformative potential—they promise enhanced liquidity flow , broader accessibility ,and increased resilience within digital finance—but must navigate complex technical hurdles along with evolving legal landscapes.
Staying informed about ongoing developments, understanding underlying technologies like cross-chain bridges & layer 2 solutions—and assessing associated risks—is essential whether you're an investor looking into new opportunities or developer aiming at building next-generation DeFi applications.
By fostering collaboration among stakeholders—including regulators—to establish best practices will be key in realizing fully functional interoperable digital currencies capable of supporting global financial inclusion efforts effectively.
Keywords:chain agnostic stablecoin | interoperable cryptocurrency | cross-chain protocol | DeFi integration | blockchain interoperability | multi-platform token transfer
Sorumluluk Reddi:Üçüncü taraf içeriği içerir. Finansal tavsiye değildir.
Hüküm ve Koşullar'a bakın.
What Are Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins?
Understanding Stablecoins and Their Limitations
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a stable value, typically pegged to fiat currencies like the US dollar. They serve as a bridge between traditional finance and the digital asset world, providing stability in an otherwise volatile market. Popular examples include Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC), which are primarily issued on Ethereum. While these stablecoins have facilitated many DeFi applications, their reliance on specific blockchain networks limits their flexibility. Users often face challenges when transferring assets across different blockchains, leading to increased transaction costs and complexity.
The Rise of Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins
Chain-agnostic stablecoins address these limitations by enabling interoperability across multiple blockchain platforms. Unlike traditional stablecoins tied to a single network, chain-agnostic versions can operate seamlessly on various blockchains such as Ethereum, Solana, Polkadot, Cosmos, and others. This flexibility is achieved through advanced cross-chain protocols that facilitate secure asset transfers without intermediaries.
These innovations are crucial for expanding DeFi ecosystems because they allow users to leverage different blockchain features—such as faster transaction speeds or lower fees—without sacrificing access to stable assets. As the demand for decentralized financial services grows, so does the need for more versatile stablecoin solutions that can adapt across diverse blockchain environments.
How Do Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins Work?
At their core, chain-agnostic stablecoins rely on interoperability protocols that enable cross-chain communication. Protocols like Polkadot’s parachains or Cosmos’ IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication) facilitate secure transfer of tokens between different networks by creating bridges or wrapped tokens representing assets from one chain on another.
For example:
- A user can lock US dollars in a smart contract on one blockchain.
- The protocol issues an equivalent token—say “StableCoinX”—on another compatible network.
- The user can then transact with this token within that ecosystem while maintaining its peg to the fiat currency.
This process involves complex mechanisms such as multi-signature security models and decentralized validators ensuring trustless transactions without centralized intermediaries.
Benefits of Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins
The primary advantage is enhanced interoperability; users aren’t confined to a single blockchain environment but can move funds freely across multiple platforms based on their needs. This flexibility supports more efficient trading strategies in DeFi markets where liquidity pools span various chains.
Security remains paramount; many chain-agnostic projects leverage decentralized technologies designed to minimize vulnerabilities associated with centralized exchanges or custodians typical of some traditional stablecoin issuers. Moreover, these coins contribute significantly toward reducing fragmentation within crypto markets by unifying diverse ecosystems under common financial instruments.
Challenges Facing Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins
Despite promising developments, several hurdles remain:
- Regulatory Uncertainty: As governments worldwide scrutinize cryptocurrencies more closely—including those used in cross-chain setups—compliance becomes complex due to differing jurisdictional requirements.
- Technical Complexity: Building robust cross-chain protocols demands sophisticated technology; vulnerabilities could expose users to smart contract exploits or security breaches.
- Market Adoption: Widespread acceptance depends not only on technological reliability but also regulatory clarity and community trust—a gradual process requiring ongoing innovation.4 Recent Developments Enhancing Cross-Chain Capabilities
Over recent years, significant progress has been made:
• 2020 marked initial interest with emerging cross-chain protocols gaining traction.• 2021 saw launches like TerraUSD (UST) and Frax (FRAX), which began exploring multi-platform deployment strategies.• 2022 brought maturation of infrastructure projects such as Polkadot’s parachains and Cosmos’ IBC framework facilitating smoother asset transfers.• In 2023, Solana's Wormhole protocol further expanded capabilities by enabling seamless bridging between Solana and other chains.
These advancements have contributed substantially toward making chain-agnostic stablecoins more practical for everyday use cases within DeFi applications like lending platforms (e.g., Aave), decentralized exchanges (DEXs), and yield farming services.
Potential Risks Moving Forward
As adoption increases alongside technological sophistication comes heightened regulatory scrutiny from authorities concerned about money laundering risks or consumer protection issues related to cross-border transactions involving digital assets.
Additionally,
– Security risks persist due to potential smart contract bugs or exploits targeting bridge mechanisms,– Market volatility inherent in crypto markets could impact perceived stability despite pegged values,– Regulatory compliance may impose restrictions affecting usability across jurisdictions,
Stakeholders must stay vigilant while innovating responsibly within this evolving landscape.
Future Outlook for Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins
Looking ahead, continued development of interoperable protocols promises even greater integration among diverse blockchains—potentially transforming how digital assets are used globally. As regulators clarify frameworks around cryptocurrency operations—including those involving cross-chain activities—the industry will likely see increased legitimacy fostering broader adoption among institutional investors alongside retail users.
In summary,
Chain-agnostic stablecoins represent an important evolution in cryptocurrency infrastructure by combining stability with versatility across multiple networks—a critical step toward realizing fully interconnected decentralized finance systems capable of serving global needs efficiently.
Keywords: Blockchain interoperability | Cross-chain protocols | Decentralized finance | Multi-platform stablecoin | Cryptocurrency regulation


kai
2025-05-14 12:59
What are chain-agnostic stablecoins?
What Are Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins?
Understanding Stablecoins and Their Limitations
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a stable value, typically pegged to fiat currencies like the US dollar. They serve as a bridge between traditional finance and the digital asset world, providing stability in an otherwise volatile market. Popular examples include Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC), which are primarily issued on Ethereum. While these stablecoins have facilitated many DeFi applications, their reliance on specific blockchain networks limits their flexibility. Users often face challenges when transferring assets across different blockchains, leading to increased transaction costs and complexity.
The Rise of Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins
Chain-agnostic stablecoins address these limitations by enabling interoperability across multiple blockchain platforms. Unlike traditional stablecoins tied to a single network, chain-agnostic versions can operate seamlessly on various blockchains such as Ethereum, Solana, Polkadot, Cosmos, and others. This flexibility is achieved through advanced cross-chain protocols that facilitate secure asset transfers without intermediaries.
These innovations are crucial for expanding DeFi ecosystems because they allow users to leverage different blockchain features—such as faster transaction speeds or lower fees—without sacrificing access to stable assets. As the demand for decentralized financial services grows, so does the need for more versatile stablecoin solutions that can adapt across diverse blockchain environments.
How Do Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins Work?
At their core, chain-agnostic stablecoins rely on interoperability protocols that enable cross-chain communication. Protocols like Polkadot’s parachains or Cosmos’ IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication) facilitate secure transfer of tokens between different networks by creating bridges or wrapped tokens representing assets from one chain on another.
For example:
- A user can lock US dollars in a smart contract on one blockchain.
- The protocol issues an equivalent token—say “StableCoinX”—on another compatible network.
- The user can then transact with this token within that ecosystem while maintaining its peg to the fiat currency.
This process involves complex mechanisms such as multi-signature security models and decentralized validators ensuring trustless transactions without centralized intermediaries.
Benefits of Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins
The primary advantage is enhanced interoperability; users aren’t confined to a single blockchain environment but can move funds freely across multiple platforms based on their needs. This flexibility supports more efficient trading strategies in DeFi markets where liquidity pools span various chains.
Security remains paramount; many chain-agnostic projects leverage decentralized technologies designed to minimize vulnerabilities associated with centralized exchanges or custodians typical of some traditional stablecoin issuers. Moreover, these coins contribute significantly toward reducing fragmentation within crypto markets by unifying diverse ecosystems under common financial instruments.
Challenges Facing Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins
Despite promising developments, several hurdles remain:
- Regulatory Uncertainty: As governments worldwide scrutinize cryptocurrencies more closely—including those used in cross-chain setups—compliance becomes complex due to differing jurisdictional requirements.
- Technical Complexity: Building robust cross-chain protocols demands sophisticated technology; vulnerabilities could expose users to smart contract exploits or security breaches.
- Market Adoption: Widespread acceptance depends not only on technological reliability but also regulatory clarity and community trust—a gradual process requiring ongoing innovation.4 Recent Developments Enhancing Cross-Chain Capabilities
Over recent years, significant progress has been made:
• 2020 marked initial interest with emerging cross-chain protocols gaining traction.• 2021 saw launches like TerraUSD (UST) and Frax (FRAX), which began exploring multi-platform deployment strategies.• 2022 brought maturation of infrastructure projects such as Polkadot’s parachains and Cosmos’ IBC framework facilitating smoother asset transfers.• In 2023, Solana's Wormhole protocol further expanded capabilities by enabling seamless bridging between Solana and other chains.
These advancements have contributed substantially toward making chain-agnostic stablecoins more practical for everyday use cases within DeFi applications like lending platforms (e.g., Aave), decentralized exchanges (DEXs), and yield farming services.
Potential Risks Moving Forward
As adoption increases alongside technological sophistication comes heightened regulatory scrutiny from authorities concerned about money laundering risks or consumer protection issues related to cross-border transactions involving digital assets.
Additionally,
– Security risks persist due to potential smart contract bugs or exploits targeting bridge mechanisms,– Market volatility inherent in crypto markets could impact perceived stability despite pegged values,– Regulatory compliance may impose restrictions affecting usability across jurisdictions,
Stakeholders must stay vigilant while innovating responsibly within this evolving landscape.
Future Outlook for Chain-Agnostic Stablecoins
Looking ahead, continued development of interoperable protocols promises even greater integration among diverse blockchains—potentially transforming how digital assets are used globally. As regulators clarify frameworks around cryptocurrency operations—including those involving cross-chain activities—the industry will likely see increased legitimacy fostering broader adoption among institutional investors alongside retail users.
In summary,
Chain-agnostic stablecoins represent an important evolution in cryptocurrency infrastructure by combining stability with versatility across multiple networks—a critical step toward realizing fully interconnected decentralized finance systems capable of serving global needs efficiently.
Keywords: Blockchain interoperability | Cross-chain protocols | Decentralized finance | Multi-platform stablecoin | Cryptocurrency regulation
Sorumluluk Reddi:Üçüncü taraf içeriği içerir. Finansal tavsiye değildir.
Hüküm ve Koşullar'a bakın.
What Are Stablecoins and Why Are They Important in Cryptocurrency?
Stablecoins are a unique class of digital assets designed to maintain a stable value, typically pegged to traditional fiat currencies like the US dollar, euro, or yen. Unlike Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are known for their price volatility, stablecoins aim to provide the stability necessary for everyday transactions and trading activities within the crypto ecosystem. This stability is achieved through various mechanisms such as collateralization with reserves or algorithmic adjustments.
In essence, stablecoins serve as a bridge between traditional finance and cryptocurrencies. They allow users to transfer value quickly across borders without the need for banks or intermediaries while avoiding the wild price swings common in other cryptocurrencies. This makes them particularly valuable for traders seeking safe havens during volatile market conditions and for DeFi platforms that require reliable liquidity pools.
Types of Stablecoins: How Do They Work?
There are several types of stablecoins based on their backing mechanisms:
- Fiat-Collateralized Stablecoins: These are backed by reserves of fiat currency held in bank accounts or custodial wallets. For example, Tether (USDT) claims to hold US dollars equivalent to its circulating tokens.
- Commodity-Backed Stablecoins: These are backed by physical commodities such as gold or silver. An example includes gold-backed tokens that represent ownership of physical precious metals.
- Algorithmic Stablecoins: Instead of holding reserves, these rely on algorithms and smart contracts to control supply dynamically based on market demand—examples include TerraUSD (UST) before its collapse and Frax (FRAX).
Each type has its advantages and risks; fiat-backed coins tend to be more stable but face regulatory scrutiny regarding reserve transparency. Algorithmic coins offer higher yields but can be more susceptible to failure if their underlying algorithms malfunction.
The Role of Stablecoins in Cryptocurrency Trading
Stablecoins have become essential tools within cryptocurrency markets due to their ability to mitigate volatility risks. Traders often convert volatile assets into stablecoins during downturns so they can preserve capital without cashing out into traditional currencies—this process is called "stablecoin hedging."
Additionally, many decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols depend heavily on stablecoin liquidity pools for lending, borrowing, yield farming, and liquidity provision activities. Platforms like Uniswap and Aave facilitate seamless swaps involving stablecoins because they provide predictable pricing environments compared with highly volatile cryptocurrencies.
Moreover, exchanges use stablecoin trading pairs extensively because they enable smoother transactions without exposing traders directly to crypto market fluctuations.
Recent Trends Shaping the Stablecoin Landscape
The past few years have seen rapid growth in both adoption and innovation surrounding stablecoins:
Regulatory Developments
Regulators worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing how stablecoin issuers manage reserves and ensure transparency. In 2022 alone, U.S regulators like the SEC launched investigations into Tether’s reserve claims—a move aimed at increasing industry accountability. Similarly, European authorities proposed stricter regulations targeting issuer disclosures & consumer protections.
Market Expansion
The total market capitalization of all stablecoins surpassed $150 billion by mid-2023—a testament not only to growing adoption but also increased integration with mainstream financial systems via partnerships with payment providers & institutional investors.
Innovation Through Algorithmic Coins
While algorithmic coins promised higher yields through automated supply adjustments—like TerraUSD—they also demonstrated significant vulnerabilities when confidence eroded following Terra’s collapse in May 2022. This event underscored inherent risks associated with complex algorithms that lack sufficient collateral backing.
CBDCs Impacting Stability
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), issued directly by governments’ central banks using blockchain technology—are viewed both as competitors & complements within this space; some experts believe CBDCs could replace certain functions traditionally served by private-issued stablecoins due to enhanced security & regulation compliance.
Risks Facing Stablecoin Ecosystem Today
Despite their benefits—and growing importance—the stability-focused nature of these assets exposes them repeatedly to specific risks:
Regulatory Risks: Governments may impose restrictions or bans if they perceive threats related primarily around money laundering concerns or financial stability issues.
Market Volatility: The failure of algorithmic models like TerraUSD highlights how reliance on uncollateralized mechanisms can lead rapidly toward loss of peg integrity.
Liquidity Concerns: Sudden mass withdrawals could cause liquidity crunches affecting broader markets since many DeFi protocols depend heavily on large-scale holdings.
Security Vulnerabilities: Smart contract bugs or reserve mismanagement pose significant threats; breaches could result in substantial losses impacting user trust across platforms.
These challenges emphasize why ongoing regulation development combined with technological safeguards remains critical for sustainable growth within this sector.
How Regulation Is Shaping Future Use Cases
As regulatory frameworks evolve globally—including proposals from entities such as the EU’s Markets in Crypto-assets Regulation (MiCA)—the future landscape will likely see increased oversight over issuance practices & reserve transparency standards among issuers like Tether & Circle's USD Coin (USDC).
This shift aims not only at protecting consumers but also at integrating digital assets more seamlessly into conventional financial systems—potentially paving way for wider acceptance among institutions wary about exposure risk associated with unregulated tokens.
The Future Outlook: Opportunities And Challenges Ahead
Stablecoins continue playing an integral role amid ongoing innovations such as CBDCs which might redefine digital monetary systems altogether while offering new avenues for cross-border payments & remittances at lower costs than traditional banking channels.
However—and despite promising prospects—the ecosystem must address persistent issues including regulatory uncertainty & technological vulnerabilities before achieving widespread mainstream adoption fully aligned with global financial standards.
By understanding what stabilizes these digital assets—and recognizing both their potential benefits along with inherent risks—investors , developers , regulators ,and users can better navigate this rapidly evolving space responsibly while fostering innovation rooted firmly in trustworthiness.
Keywords: cryptocurrency ecosystem stabilization | types of stable coins | DeFi liquidity | crypto regulation trends | algorithmic vs fiat-backed coins


kai
2025-06-09 05:25
What role do stablecoins play in the cryptocurrency ecosystem?
What Are Stablecoins and Why Are They Important in Cryptocurrency?
Stablecoins are a unique class of digital assets designed to maintain a stable value, typically pegged to traditional fiat currencies like the US dollar, euro, or yen. Unlike Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are known for their price volatility, stablecoins aim to provide the stability necessary for everyday transactions and trading activities within the crypto ecosystem. This stability is achieved through various mechanisms such as collateralization with reserves or algorithmic adjustments.
In essence, stablecoins serve as a bridge between traditional finance and cryptocurrencies. They allow users to transfer value quickly across borders without the need for banks or intermediaries while avoiding the wild price swings common in other cryptocurrencies. This makes them particularly valuable for traders seeking safe havens during volatile market conditions and for DeFi platforms that require reliable liquidity pools.
Types of Stablecoins: How Do They Work?
There are several types of stablecoins based on their backing mechanisms:
- Fiat-Collateralized Stablecoins: These are backed by reserves of fiat currency held in bank accounts or custodial wallets. For example, Tether (USDT) claims to hold US dollars equivalent to its circulating tokens.
- Commodity-Backed Stablecoins: These are backed by physical commodities such as gold or silver. An example includes gold-backed tokens that represent ownership of physical precious metals.
- Algorithmic Stablecoins: Instead of holding reserves, these rely on algorithms and smart contracts to control supply dynamically based on market demand—examples include TerraUSD (UST) before its collapse and Frax (FRAX).
Each type has its advantages and risks; fiat-backed coins tend to be more stable but face regulatory scrutiny regarding reserve transparency. Algorithmic coins offer higher yields but can be more susceptible to failure if their underlying algorithms malfunction.
The Role of Stablecoins in Cryptocurrency Trading
Stablecoins have become essential tools within cryptocurrency markets due to their ability to mitigate volatility risks. Traders often convert volatile assets into stablecoins during downturns so they can preserve capital without cashing out into traditional currencies—this process is called "stablecoin hedging."
Additionally, many decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols depend heavily on stablecoin liquidity pools for lending, borrowing, yield farming, and liquidity provision activities. Platforms like Uniswap and Aave facilitate seamless swaps involving stablecoins because they provide predictable pricing environments compared with highly volatile cryptocurrencies.
Moreover, exchanges use stablecoin trading pairs extensively because they enable smoother transactions without exposing traders directly to crypto market fluctuations.
Recent Trends Shaping the Stablecoin Landscape
The past few years have seen rapid growth in both adoption and innovation surrounding stablecoins:
Regulatory Developments
Regulators worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing how stablecoin issuers manage reserves and ensure transparency. In 2022 alone, U.S regulators like the SEC launched investigations into Tether’s reserve claims—a move aimed at increasing industry accountability. Similarly, European authorities proposed stricter regulations targeting issuer disclosures & consumer protections.
Market Expansion
The total market capitalization of all stablecoins surpassed $150 billion by mid-2023—a testament not only to growing adoption but also increased integration with mainstream financial systems via partnerships with payment providers & institutional investors.
Innovation Through Algorithmic Coins
While algorithmic coins promised higher yields through automated supply adjustments—like TerraUSD—they also demonstrated significant vulnerabilities when confidence eroded following Terra’s collapse in May 2022. This event underscored inherent risks associated with complex algorithms that lack sufficient collateral backing.
CBDCs Impacting Stability
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), issued directly by governments’ central banks using blockchain technology—are viewed both as competitors & complements within this space; some experts believe CBDCs could replace certain functions traditionally served by private-issued stablecoins due to enhanced security & regulation compliance.
Risks Facing Stablecoin Ecosystem Today
Despite their benefits—and growing importance—the stability-focused nature of these assets exposes them repeatedly to specific risks:
Regulatory Risks: Governments may impose restrictions or bans if they perceive threats related primarily around money laundering concerns or financial stability issues.
Market Volatility: The failure of algorithmic models like TerraUSD highlights how reliance on uncollateralized mechanisms can lead rapidly toward loss of peg integrity.
Liquidity Concerns: Sudden mass withdrawals could cause liquidity crunches affecting broader markets since many DeFi protocols depend heavily on large-scale holdings.
Security Vulnerabilities: Smart contract bugs or reserve mismanagement pose significant threats; breaches could result in substantial losses impacting user trust across platforms.
These challenges emphasize why ongoing regulation development combined with technological safeguards remains critical for sustainable growth within this sector.
How Regulation Is Shaping Future Use Cases
As regulatory frameworks evolve globally—including proposals from entities such as the EU’s Markets in Crypto-assets Regulation (MiCA)—the future landscape will likely see increased oversight over issuance practices & reserve transparency standards among issuers like Tether & Circle's USD Coin (USDC).
This shift aims not only at protecting consumers but also at integrating digital assets more seamlessly into conventional financial systems—potentially paving way for wider acceptance among institutions wary about exposure risk associated with unregulated tokens.
The Future Outlook: Opportunities And Challenges Ahead
Stablecoins continue playing an integral role amid ongoing innovations such as CBDCs which might redefine digital monetary systems altogether while offering new avenues for cross-border payments & remittances at lower costs than traditional banking channels.
However—and despite promising prospects—the ecosystem must address persistent issues including regulatory uncertainty & technological vulnerabilities before achieving widespread mainstream adoption fully aligned with global financial standards.
By understanding what stabilizes these digital assets—and recognizing both their potential benefits along with inherent risks—investors , developers , regulators ,and users can better navigate this rapidly evolving space responsibly while fostering innovation rooted firmly in trustworthiness.
Keywords: cryptocurrency ecosystem stabilization | types of stable coins | DeFi liquidity | crypto regulation trends | algorithmic vs fiat-backed coins
Sorumluluk Reddi:Üçüncü taraf içeriği içerir. Finansal tavsiye değildir.
Hüküm ve Koşullar'a bakın.
🔥 L’activité stablecoin explose en Europe ! 🇪🇺
💥 Les transactions de stablecoins sur $ETH/USDT et $SOL/USDT ont bondi ces derniers jours pour atteindre 8,8 millions, représentant désormais 36 % de toutes les transactions mondiales.
💡 Ce boom illustre la montée en puissance de l’adoption crypto en Europe, portée par la régulation MiCA et la confiance accrue dans les paiements on-chain.
👉 Les stablecoins ne dorment plus : ils redessinent le futur du paiement numérique.
#stablecoins #CryptoNews #blockchain #cryptocurrency


Carmelita
2025-10-25 18:30
🔥 L’activité stablecoin explose en Europe ! 🇪🇺�
Sorumluluk Reddi:Üçüncü taraf içeriği içerir. Finansal tavsiye değildir.
Hüküm ve Koşullar'a bakın.