牛市结束了吗?
现在市场有两个主流声音:
1. 见顶派:这一轮牛市已见顶
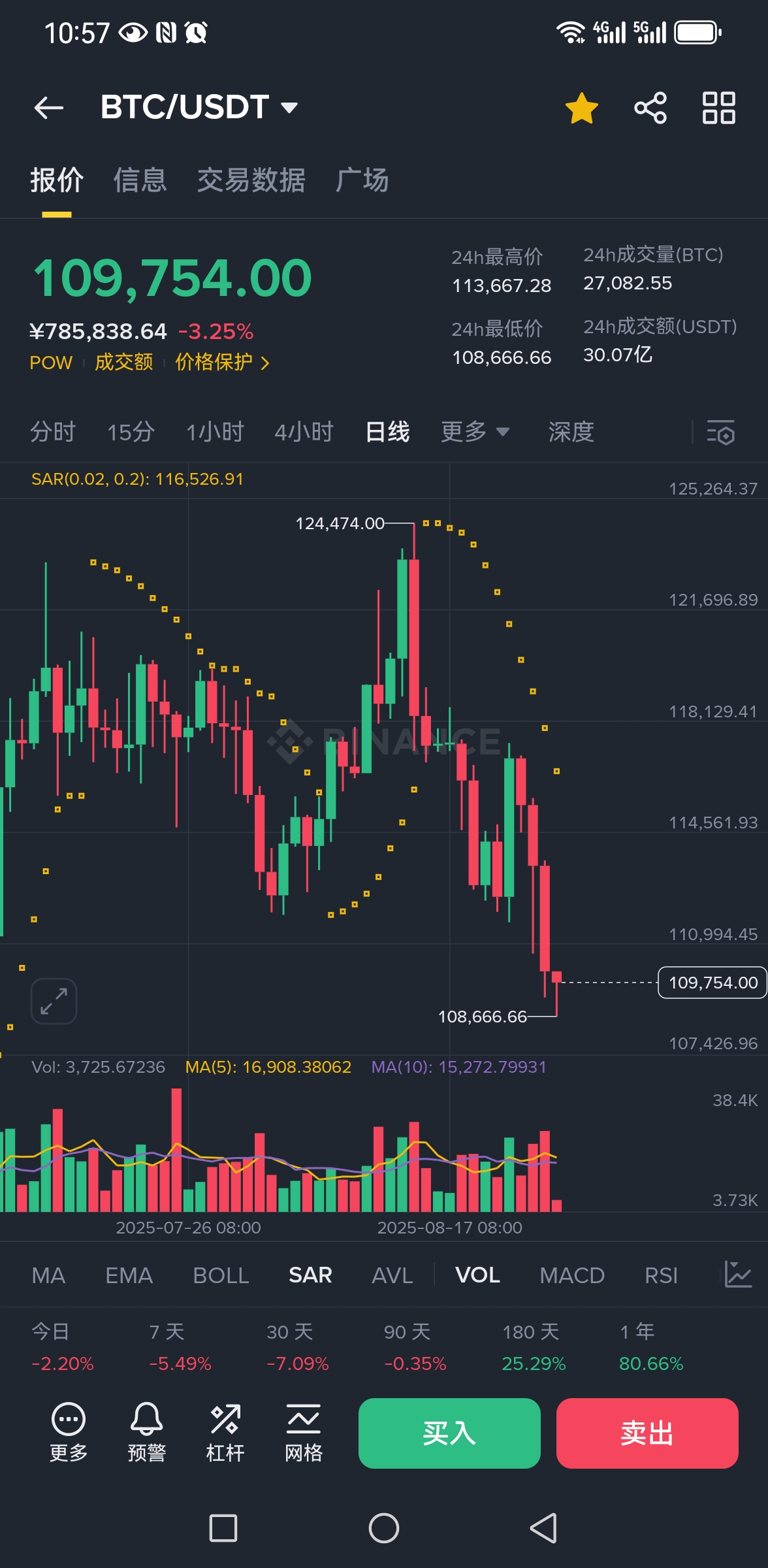
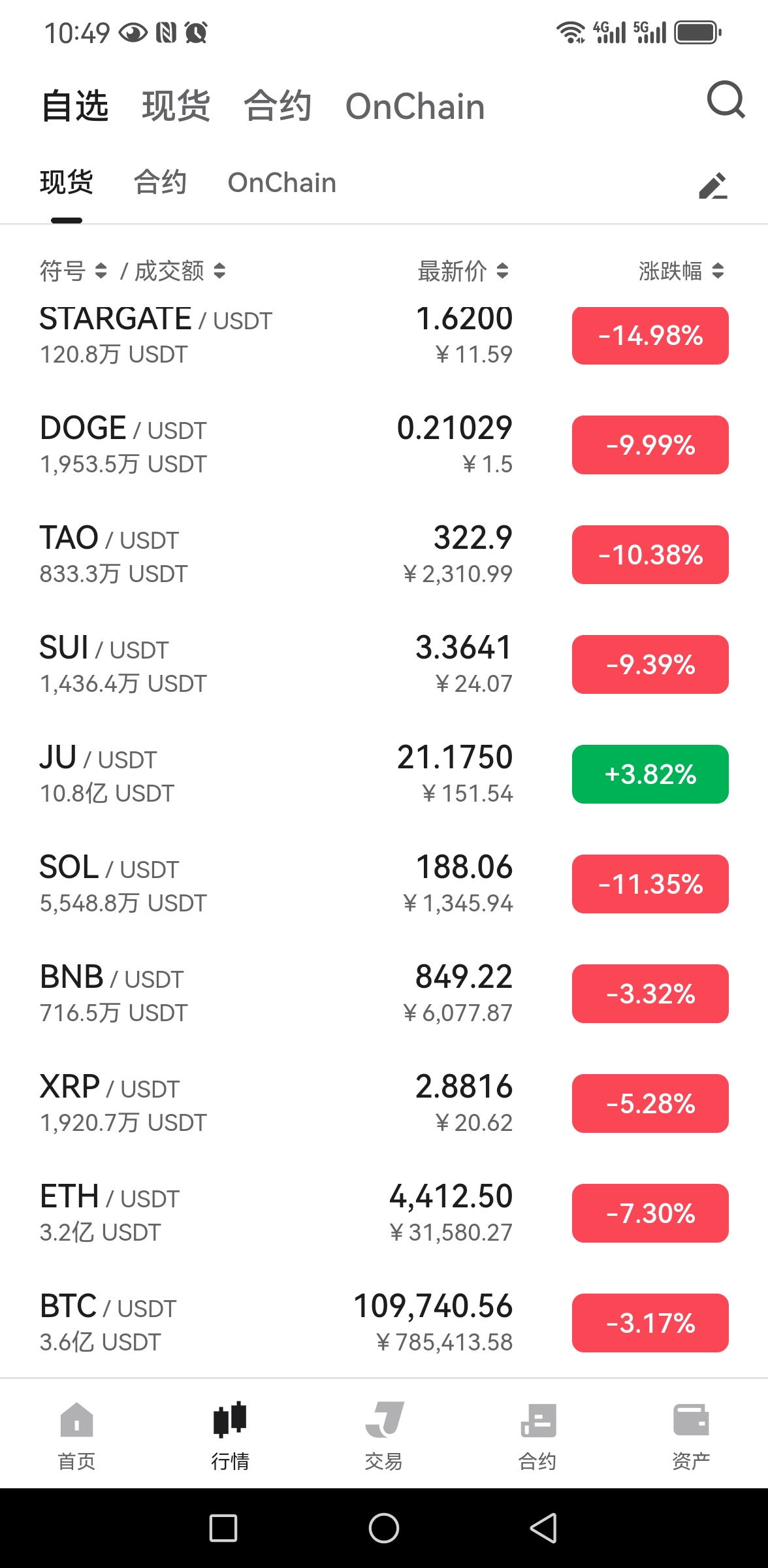
理由:BTC周线顶背离+MACD死叉,比特币十年以上OG频繁出货,大户清仓,比特币ETF资金持续净流出。
2.疯牛派,大的要来了
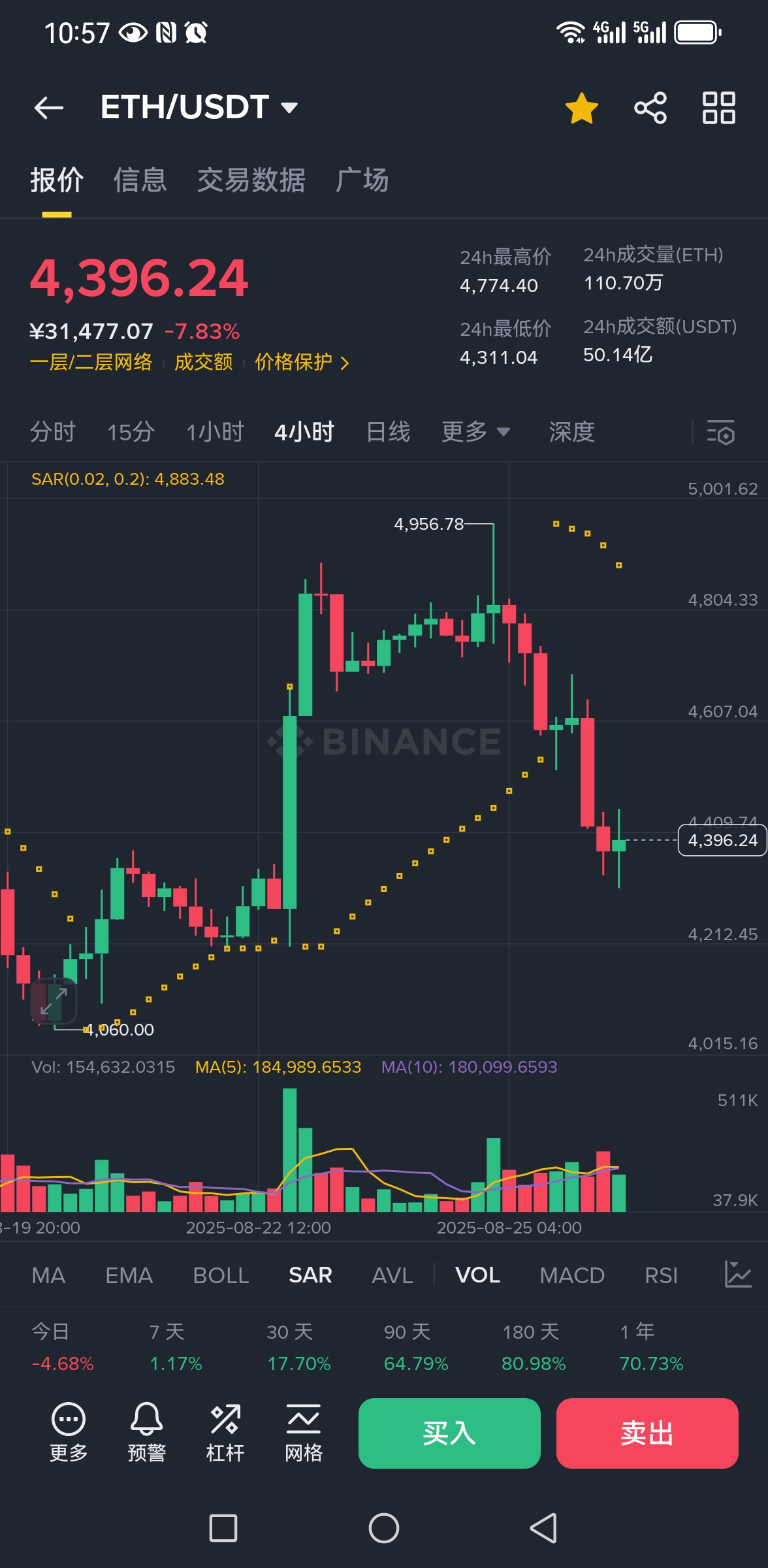
山寨季要来临,依据4年周期论,目前BTC见顶暴跌,资金流出到ETH和山寨,接下来ETH和山寨将最后疯涨3-4个月,9月降息提供流动性支持,狂暴大牛市来了你无法想象。
我们社区的观点:8月底和9月上旬先暴跌一波把疯牛派满仓期待的山寨季干成山寨祭,让见顶派嚣张一段时间,把疯牛派洗到绝望,等降息落地流动性释放,ETH带领山寨迎来最后一波行情,把见顶派和疯牛派彻底涨服,让他们FOMO上车再砸盘,一起套在山顶。
理由就是现在基本面的问题:之前回调洗盘不彻底没完成,被鲍威尔奶了一口,ETH带领山寨币打了一针鸡血,但是比特币没有太大反应,现在又跌出新低(比特币机构化,比散户集中的山寨更冷静);
以前也说过,事件引起的涨跌最终都会回归正常,只是延长或者推迟了原本的进程。
现在美联储9月降息还没有落地,并且降息的资金流进市场也需要时间,这两个问题留下的时间差,主力肯定会用来洗盘!因为现在车太重。
所以现在应该是预防大跌洗盘的阶段,而不是幻想新高的事情,见好就收依然是主题。
这一段时间我像个空军头子!只是因为经历过5.19/3.12,见过太多吃人不吐骨头的时刻,牛市里韭菜亏的比熊市里更多、更惨,因为牛市给了太多人不切实际的幻想。
当然,就算是今年3月、4月大跌时,我也说过,今年下半年的牛市该来的都会来,就看你有没有勇气越跌越买,然后到时候越涨越卖,这个市场会止盈其实才是更重要的事情---这是韭菜与高手的根本区别。


晴朗财经
2025-08-26 03:03
牛市结束了吗?
免责声明:含第三方内容,非财务建议。
详见《条款和条件》



What Is the Total Number of Transactions on the Bitcoin Network?
Understanding the total number of transactions on the Bitcoin network is essential for grasping how active and widely used this pioneering cryptocurrency truly is. This metric offers insights into user engagement, network health, and overall adoption trends. In this article, we will explore what influences transaction volume, recent developments in 2023, and what these figures mean for investors and users alike.
How Does Transaction Volume Reflect Network Activity?
The total number of Bitcoin transactions indicates how frequently users are transferring funds or engaging with blockchain-based applications. On average, as of 2023, around 250,000 to 300,000 transactions occur daily. These fluctuations are driven by various factors such as market sentiment—bullish periods tend to see increased activity—as well as regulatory environments that can either encourage or restrict usage.
High transaction volumes suggest a vibrant ecosystem where users actively buy, sell, or transfer Bitcoin. Conversely, dips may signal reduced interest or external pressures like stricter regulations. Monitoring these numbers helps stakeholders gauge whether Bitcoin remains a popular medium for peer-to-peer payments or speculative trading.
Factors Influencing Transaction Counts
Several key elements impact how many transactions are recorded on the blockchain:
- Market Conditions: Bull markets often lead to increased trading activity as investors seek opportunities.
- Regulatory Changes: Stricter laws can temporarily suppress transaction volumes; conversely, favorable policies may boost activity.
- Network Congestion: When many users transact simultaneously—such as during major price swings—transaction fees rise due to limited block space.
- Technological Developments: Improvements like SegWit (Segregated Witness) have optimized transaction processing times and costs over time.
These factors collectively shape daily transaction counts and influence user behavior across different periods.
Recent Trends in 2023: Fluctuations in Transaction Numbers
In April 2023, the Bitcoin network experienced a notable surge in transaction volume driven by heightened market speculation amid potential regulatory shifts in major economies. This increase was partly fueled by traders reacting to news about possible government interventions that could impact cryptocurrency markets globally.
However, May saw an uptick in average transaction fees—about a 20% rise compared to previous months—which reflects higher network congestion. Elevated fees can discourage smaller transactions from occurring frequently because they become less cost-effective for everyday use cases like micro-payments or casual transfers.
These recent trends highlight how external events directly influence not only how much activity occurs but also its economic viability for typical users.
Blockchain Size and Its Impact on Transactions
The size of the Bitcoin blockchain itself provides context about overall network activity; it stood at approximately 400 GB in early 2023—a significant increase from previous years due to continuous addition of new blocks containing transactional data.
A larger blockchain signifies more historical data stored across nodes worldwide but also raises concerns regarding scalability:
- Larger blockchains require more storage capacity.
- Synchronization times increase for new nodes joining the network.
- Higher data loads can contribute to slower confirmation times during peak periods unless scaling solutions are implemented effectively.
Efforts such as Lightning Network aim to address these scalability challenges by enabling faster off-chain transactions while maintaining security through underlying blockchain settlement layers.
The Role of Miners and Validation Processes
Miners play a crucial role in maintaining accurate records by validating transactions through complex computational puzzles—a process known as proof-of-work (PoW). They compete within seconds to add new blocks containing pending transactions onto the chain; successful miners receive rewards plus associated fees paid by transacting parties.
This validation process ensures integrity but is energy-intensive: estimates suggest that mining consumes substantial electricity globally. As demand increases with higher transaction volumes during active periods like April-May 2023’s surge,
the environmental footprint becomes more prominent concern among regulators and advocates alike.
Key Points About Mining:
- Miners validate hundreds of thousands of daily transactions
- Validation ensures decentralization & security
- Rising demand impacts energy consumption
Regulatory Environment's Effect on Transaction Volumes
Government policies significantly influence user participation levels on the Bitcoin network. In early 2023,
several countries introduced stricter regulations targeting crypto exchanges,which temporarily dampened trading activities reflected through decreased transaction counts initially observed after policy announcements.
However,
some jurisdictions adopted clearer frameworks encouraging institutional involvement,potentially stabilizing or increasing future transactional activity once compliance mechanisms were established.
Summary:
Regulatory uncertainty remains one of the most unpredictable factors affecting total bitcoin transactions; ongoing legislative developments will continue shaping usage patterns moving forward.
Future Outlook: Scalability Solutions & Adoption Trends
As interest grows among retail investors and institutions alike,
scalability solutions such as Taproot upgrades,Lightning Network implementations,and sidechains aim to facilitate faster processing at lower costs.
These technological advancements could help sustain higher throughput levels necessary for mainstream adoption while reducing congestion-related fee hikes seen earlier this year.
Moreover,
wider acceptance from merchants accepting bitcoin payments directly enhances real-world utility beyond speculative trading,
potentially leading toward sustained growth in total number of daily transactions over coming years.
By continuously monitoring metrics like total bitcoin transaction count alongside technological improvements and regulatory changes,
stakeholders—from individual users to large-scale investors—can better understand market dynamics
and make informed decisions aligned with evolving industry conditions.
References
- CoinDesk — General information on Bitcoin networks
- Blockchain.com Charts — Historical data analysis
- Blockchain Size Data — Blockchain growth insights
- Transaction Fees & Congestion — Impact analysis
- Bitcoin Mining Process — Technical validation overview
- Regulatory Impact Reports — Policy effects assessment
Understanding how many people transact using Bitcoin provides valuable insight into its current state—and future potential—as both an investment asset and a decentralized payment system amidst an ever-changing global landscape
What Are Common Cryptocurrency Scams?
Cryptocurrency scams have become an increasingly prevalent threat in the digital financial landscape. As the popularity of cryptocurrencies continues to grow, so does the sophistication and variety of scams targeting investors—both newcomers and seasoned traders. Understanding these common scams is essential for protecting your assets and making informed decisions in this volatile market.
Phishing Scams: How Cybercriminals Steal Sensitive Information
Phishing remains one of the most widespread cryptocurrency scams. It involves tricking individuals into revealing private keys, passwords, or seed phrases through fake websites, emails, or social media messages that closely mimic legitimate platforms. Attackers often craft convincing messages that prompt users to click malicious links or provide confidential information under false pretenses.
In recent years, phishing campaigns targeting crypto users have resulted in millions of dollars stolen from victims worldwide. These attacks are frequently linked with malware and ransomware infections that further compromise user security. To avoid falling victim to phishing, always verify website URLs carefully, enable two-factor authentication (2FA), and remain cautious about unsolicited communications requesting sensitive data.
Ponzi Schemes: Promises of High Returns with No Real Revenue
Ponzi schemes are fraudulent investment operations that promise high returns with little risk but rely on new investor funds to pay existing investors rather than generating legitimate profits. In the cryptocurrency space, these schemes often promote fake investment platforms claiming guaranteed gains through complex algorithms or proprietary tokens.
In 2024 alone, authorities exposed several crypto-related Ponzi schemes leading to significant financial losses for participants. These schemes typically attract charismatic leaders who build trust by offering seemingly lucrative opportunities before collapsing once new investments dry up—leaving many investors empty-handed.
To identify potential Ponzi schemes:
- Be wary of promises guaranteeing high returns with minimal risk.
- Investigate whether the platform has transparent operations.
- Check if regulatory bodies have issued warnings against such platforms.
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) Scams: Fake Projects That Promise Big Rewards
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) were once a popular method for startups to raise capital by issuing new tokens directly to investors. Unfortunately, this market has been exploited by scammers launching fraudulent ICOs promising substantial profits without any real product or backing.
The lack of regulation during certain periods made it easier for scammers to launch fake projects—resulting in millions lost by unsuspecting investors in 2022 alone. Although regulatory agencies like the SEC have increased oversight and issued warnings about unregistered ICOs, many scam projects still slip through enforcement cracks.
Investors should conduct thorough due diligence before participating:
- Verify project teams’ backgrounds.
- Review whitepapers critically.
- Confirm registration status with relevant authorities when possible.
Fake Trading Platforms: When Looks Can Be Deceiving
Fake trading platforms lure users with promises of high returns but are designed solely to steal funds once deposits are made. These sites often feature professional-looking interfaces mimicking reputable exchanges but lack proper security measures or licensing credentials.
In 2023 alone, multiple fake trading platforms were shut down after defrauding countless traders out of their investments—a pattern that continues as scammers develop more convincing replicas regularly. Victims typically report losing large sums after depositing money into these illegitimate sites; some never recover their funds due to untraceable transactions or platform shutdowns.
To protect yourself:
- Use well-known exchanges regulated within your jurisdiction.
- Look for secure website indicators like HTTPS certificates.
- Avoid deals that seem too good to be true without verifying legitimacy thoroughly.
Social Engineering Attacks: Manipulating Human Psychology
Social engineering exploits human psychology rather than technical vulnerabilities by manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information or performing actions detrimental to their security—for example, transferring funds based on false instructions received via email or social media messages from impersonators pretending as trusted contacts or officials.
In 2024’s notable cases involving social engineering tactics targeting crypto users resulted in thefts totaling millions of dollars globally. Attackers often leverage fear tactics ("Your account will be suspended") or urgency ("Send funds immediately") strategies designed specifically around psychological pressure points common among less experienced investors who may not recognize manipulation cues readily.
Key Techniques Include:
- Impersonation via email (spoofed addresses)
- Pretexting through phone calls
- Fake official notices on social media
How To Protect Yourself
- Always verify identities independently before acting on requests.
- Enable multi-layered authentication processes.
- Stay skeptical about unsolicited communication demanding urgent action.
Rug Pulls: When Developers Abandon Projects Suddenly
Rug pulls refer to scenarios where project creators abruptly withdraw liquidity from a DeFi protocol—or abandon a project altogether—leaving investors holding worthless tokens overnight. This scam is particularly prevalent within decentralized finance spaces where transparency can be limited unless properly audited.
Recent reports from 2023 highlight numerous rug pulls resulting in substantial losses across various DeFi projects; scammers exploit hype cycles and insufficient vetting processes among retail investors eager for quick gains.
Signs Of A Potential Rug Pull
- Lack of transparency regarding team members
- Sudden withdrawal announcements
- Unverified smart contracts lacking audits
Preventive Measures
Investors should prioritize projects with verified codebases and independent audits while avoiding anonymous developers promising unrealistic yields.
Recent Trends & Developments in Cryptocurrency Scam Prevention
The rise in cybercrime activity correlates strongly with increasing cryptocurrency values; cybercriminals stole approximately $16.6 billion globally in 2024—a significant jump compared even just a few years prior[1]. Notably targeted groups include seniors vulnerable due to limited tech literacy who fall prey mainly through investment scams and tech support fraud[1].
Regulatory efforts are intensifying worldwide as governments implement stricter rules against unregistered offerings like ICO frauds while cracking down on illegal trading platforms[reuters.com]. Simultaneously, educational initiatives aim at raising awareness among users about common scam tactics—empowering them against deception[coindesk.com].
Technological advancements also play a vital role; innovations such as multi-signature wallets enhance transaction security while AI-driven cybersecurity tools help detect suspicious activities proactively[securitymagazine.com].
Staying vigilant remains crucial amid evolving threats within the cryptocurrency ecosystem—from understanding scam types like phishing and rug pulls—to adopting best practices such as verifying sources thoroughly before investing online can significantly reduce risks associated with these digital assets' volatile environment.
References
1. Cybercriminals stole $16..6 billion
3. Malware & Ransomware Insights
4. Crypto Ponzi Scheme Exposures
5. Understanding Ponzi Schemes
7. [Regulatory Warnings & Actions](https://www.sec.gov/news/press-release /2023‑1234)
8. Fake Trading Platforms & Risks
9. [Cybersecurity Threat Reports](https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles /2023‑05‑10/fake‑crypto-trading-platforms-target-investors)
10. Social Engineering Tactics
11. [Rug Pull Incidents & Analysis](https://www.coindesk.com /markets /2023 /08 /15/rug-pull/)
12. [Crypto Regulation Updates](https://www.reuters .com/article/us -crypto-regulation-idUSKBN2JL1JL)
13. [Educational Campaign Initiatives ]( https :// www.coindesk .com /markets / 20 23 /10 /15 /educational -initiatives )
